Synergistic Activity of Paclitaxel, Sorafenib, and Radiation Therapy in advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma and Breast Cancer
- PMID: 30522045
- PMCID: PMC6279801
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2018.11.007
Synergistic Activity of Paclitaxel, Sorafenib, and Radiation Therapy in advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma and Breast Cancer
Abstract
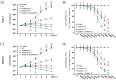
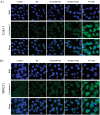
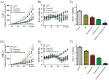
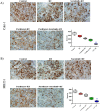
Advanced cancer has been shown to be associated with a higher percentage of epigenetic changes than with genetic mutations. Preclinical models have shown that the combination of paclitaxel, sorafenib, and radiation therapy (RT) plays a crucial role in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and breast cancer. This study aimed to investigate the involvement of mitochondrial cytochrome c-dependent apoptosis in the mechanism of action of a combination of paclitaxel, sorafenib, and RT in RCC and breast cancer. RCC and breast cancer cell lines were exposed to paclitaxel and sorafenib alone or combined in the presence of radiation, and cell viability was determined using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. The synergistic anticancer effects of the combination therapy on cell cycle and intracellular signaling pathways were estimated using flow cytometry and immunoblot analysis. RCC and breast cancer cell line xenograft models were used to examine the antitumor activity in vivo. Our results suggest that paclitaxel, sorafenib, and RT synergistically decreased the viability of RCC and breast cancer cells and significantly induced their apoptosis, as shown by caspase-3 cleavage. Paclitaxel, sorafenib, and radiation cotreatment reduced antiapoptotic factor levels in these cells and, thereby, significantly reduced the tumor volume of RCC and breast cancer cell xenografts. The current study suggests that paclitaxel, sorafenib, and radiation cotreatment was more effective than cotreatment with paclitaxel or sorafenib and radiation. These findings may offer a new therapeutic approach to RCC and breast cancer.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synergistic anticancer activity of sorafenib, paclitaxel, and radiation therapy on anaplastic thyroid cancer in vitro and in vivo.Head Neck. 2020 Dec;42(12):3678-3684. doi: 10.1002/hed.26431. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Head Neck. 2020. PMID: 32896015
-
Synergistic Anticancer Activity of N-Hydroxy-7-(2-Naphthylthio) Heptanomide, Sorafenib, and Radiation Therapy in Patient-Derived Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 7;22(2):536. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020536. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33430361 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin combined with sorafenib synergistically inhibit the invasive ability through targeting metastasis-associated protein 2 expression in human renal cancer cells.Tzu Chi Med J. 2021 Oct 21;34(2):192-199. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_204_21. eCollection 2022 Apr-Jun. Tzu Chi Med J. 2021. PMID: 35465276 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Activity of N-hydroxy-7-(2-naphthylthio) Heptanomide and Sorafenib Against Cancer Stem Cells, Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer.Neoplasia. 2017 Mar;19(3):145-153. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2016.12.005. Epub 2017 Jan 28. Neoplasia. 2017. PMID: 28142087 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical experience and critical evaluation of the role of sorafenib in renal cell carcinoma.Open Access J Urol. 2011 May 10;3:69-82. doi: 10.2147/OAJU.S7230. Open Access J Urol. 2011. PMID: 24198638 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-Omics Profiling Suggesting Intratumoral Mast Cells as Predictive Index of Breast Cancer Lung Metastasis.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 17;11:788778. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.788778. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35111673 Free PMC article.
-
Paclitaxel and Sorafenib: The Effective Combination of Suppressing the Self-Renewal of Cancer Stem Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 26;12(6):1360. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061360. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32466563 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of the metabolic reprogramming-associated gene signature for clear cell renal cell carcinoma prognosis prediction.BMC Urol. 2023 Sep 15;23(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12894-023-01317-3. BMC Urol. 2023. PMID: 37715154 Free PMC article.
-
Paclitaxel-Based Chemotherapy Targeting Cancer Stem Cells from Mono- to Combination Therapy.Biomedicines. 2021 May 2;9(5):500. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9050500. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34063205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of cancer cell death induction by paclitaxel: an updated review.Apoptosis. 2022 Oct;27(9-10):647-667. doi: 10.1007/s10495-022-01750-z. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Apoptosis. 2022. PMID: 35849264 Review.
References
-
- Michaloglou C, Vredeveld LC, Mooi WJ, Peeper DS. BRAF(E600) in benign and malignant human tumours. Oncogene. 2008;27(7):877–895. - PubMed
-
- Altomare DA, Testa JR. Perturbations of the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene. 2005;24(50):7455–7464. - PubMed
-
- Gerber DE. Targeted therapies: a new generation of cancer treatments. Am Fam Physician. 2008;77(3):311–319. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

