Mechanisms Underlying Microbial-Mediated Changes in Social Behavior in Mouse Models of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- PMID: 30522820
- PMCID: PMC6645363
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.11.018
Mechanisms Underlying Microbial-Mediated Changes in Social Behavior in Mouse Models of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
Currently, there are no medications that effectively treat the core symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). We recently found that the bacterial species Lactobacillus (L.) reuteri reverses social deficits in maternal high-fat-diet offspring. However, whether the effect of L. reuteri on social behavior is generalizable to other ASD models and its mechanism(s) of action remains unknown. Here, we found that treatment with L. reuteri selectively rescues social deficits in genetic, environmental, and idiopathic ASD models. Interestingly, the effects of L. reuteri on social behavior are not mediated by restoring the composition of the host's gut microbiome, which is altered in all of these ASD models. Instead, L. reuteri acts in a vagus nerve-dependent manner and rescues social interaction-induced synaptic plasticity in the ventral tegmental area of ASD mice, but not in oxytocin receptor-deficient mice. Collectively, treatment with L. reuteri emerges as promising non-invasive microbial-based avenue to combat ASD-related social dysfunction.
Keywords: autism; dopamine; gut-microbiota-brain axis; microbiome; oxytocin; probiotic; social behavior; vagus nerve.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
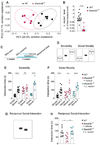

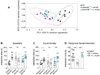
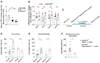
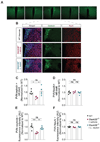

Comment in
-
Gut Microbes Join the Social Network.Neuron. 2019 Jan 16;101(2):196-198. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.12.035. Neuron. 2019. PMID: 30653931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®) (American Psychiatric Pub; ).
-
- Baio J, Wiggins L, Christensen DL, Maenner MJ, Daniels J, Warren Z, Kurzius-Spencer M, Zahorodny W, Robinson Rosenberg C, White T, et al. (2018). Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years - Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2014 Morbidity and mortality weekly report Surveillance summaries (Washington, DC: : 2002) 67, 1–23. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Drai D, Elmer G, Kafkafi N, and Golani I (2001). Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior genetics research. Behavioural brain research 125, 279–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

