Why rankings of biomedical image analysis competitions should be interpreted with care
- PMID: 30523263
- PMCID: PMC6284017
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07619-7
Why rankings of biomedical image analysis competitions should be interpreted with care
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Why rankings of biomedical image analysis competitions should be interpreted with care.Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 30;10(1):588. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08563-w. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30700735 Free PMC article.
Abstract
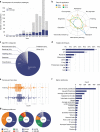
International challenges have become the standard for validation of biomedical image analysis methods. Given their scientific impact, it is surprising that a critical analysis of common practices related to the organization of challenges has not yet been performed. In this paper, we present a comprehensive analysis of biomedical image analysis challenges conducted up to now. We demonstrate the importance of challenges and show that the lack of quality control has critical consequences. First, reproducibility and interpretation of the results is often hampered as only a fraction of relevant information is typically provided. Second, the rank of an algorithm is generally not robust to a number of variables such as the test data used for validation, the ranking scheme applied and the observers that make the reference annotations. To overcome these problems, we recommend best practice guidelines and define open research questions to be addressed in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
Henning Müller is on the advisory board of “Zebra Medical Vision”. Danail Stoyanov is a paid part-time member of Touch Surgery, Kinosis Ltd. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Chen, W. Li, W. Dong, X. Pei, J. A review of biological image analysis. Curr. Bioinform. 13, 337–343 (2018).
-
- Price K. Anything you can do, I can do better (no you can’t) Comput. Gr. Image Process. 1986;36:387–391. doi: 10.1016/0734-189X(86)90083-6. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

