The emerging link between cancer, metabolism, and circadian rhythms
- PMID: 30523327
- PMCID: PMC6535395
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0271-8
The emerging link between cancer, metabolism, and circadian rhythms
Abstract
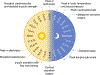
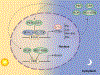
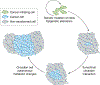
The circadian clock is a complex cellular mechanism that, through the control of diverse metabolic and gene expression pathways, governs a large array of cyclic physiological processes. Epidemiological and clinical data reveal a connection between the disruption of circadian rhythms and cancer that is supported by recent preclinical data. In addition, results from animal models and molecular studies underscore emerging links between cancer metabolism and the circadian clock. This has implications for therapeutic approaches, and we discuss the possible design of chronopharmacological strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fu L & Lee CC The circadian clock: pacemaker and tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Cancer 3, 350–361 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Sahar S & Sassone-Corsi P Metabolism and cancer: the circadian clock connection. Nat Rev Cancer 9, 886–896 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Lie JA, Roessink J & Kjaerheim K Breast cancer and night work among Norwegian nurses. Cancer Causes Control 17, 39–44 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Papantoniou K, et al. Night shift work, chronotype and prostate cancer risk in the MCCSpain case-control study. Int J Cancer 137, 1147–1157 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

