Dynamics and functions of lipid droplets
- PMID: 30523332
- PMCID: PMC6746329
- DOI: 10.1038/s41580-018-0085-z
Dynamics and functions of lipid droplets
Abstract
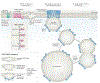
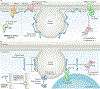
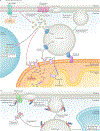
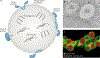
Lipid droplets are storage organelles at the centre of lipid and energy homeostasis. They have a unique architecture consisting of a hydrophobic core of neutral lipids, which is enclosed by a phospholipid monolayer that is decorated by a specific set of proteins. Originating from the endoplasmic reticulum, lipid droplets can associate with most other cellular organelles through membrane contact sites. It is becoming apparent that these contacts between lipid droplets and other organelles are highly dynamic and coupled to the cycles of lipid droplet expansion and shrinkage. Importantly, lipid droplet biogenesis and degradation, as well as their interactions with other organelles, are tightly coupled to cellular metabolism and are critical to buffer the levels of toxic lipid species. Thus, lipid droplets facilitate the coordination and communication between different organelles and act as vital hubs of cellular metabolism.
Figures

References
-
- Schaffer JE Lipotoxicity: when tissues overeat. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 14, 281–287 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Fawcett DW An Atlas of Fine Structure: The Cell, Its Organelles, and Inclusions (Saunders, 1966).
-
- Sorger D, Athenstaedt K, Hrastnik C & Daum G A yeast strain lacking lipid particles bears a defect in ergosterol formation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 31190–31196 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Sandager L et al. Storage lipid synthesis is non-essential in yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 6478–6482 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

