Select β- and γ-branched 1-alkylpyrazol-4-yl methylcarbamates exhibit high selectivity for inhibition of Anopheles gambiae versus human acetylcholinesterase
- PMID: 30524149
- PMCID: PMC6277143
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2018.02.003
Select β- and γ-branched 1-alkylpyrazol-4-yl methylcarbamates exhibit high selectivity for inhibition of Anopheles gambiae versus human acetylcholinesterase
Abstract
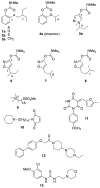
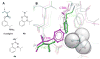
The widespread emergence of pyrethroid-resistant Anopheles gambiae has intensified the need to find new contact mosquitocides for indoor residual spraying and insecticide treated nets. With the goal of developing new species-selective and resistance-breaking acetylcholinesterase (AChE)-inhibiting mosquitocides, in this report we revisit the effects of carbamate substitution on aryl carbamates, and variation of the 1-alkyl group on pyrazol-4-yl methylcarbamates. Compared to aryl methylcarbamates, aryl dimethylcarbamates were found to have lower selectivity for An. gambiae AChE (AgAChE) over human AChE (hAChE), but improved tarsal contact toxicity to G3 strain An. gambiae. Molecular modeling studies suggest the lower species-selectivity of the aryl dimethylcarbamates can be attributed to a less flexible acyl pocket in AgAChE relative to hAChE. The improved tarsal contact toxicity of the aryl dimethylcarbamates relative to the corresponding methylcarbamates is attributed to a range of complementary phenomena. With respect to the pyrazol-4-yl methylcarbamates, the previously observed low An. gambiae-selectivity of compounds bearing α-branched 1-alkyl groups was improved by employing β- and γ-branched 1-alkyl groups. Compounds 22a (cyclopentylmethyl), 21a (cyclobutylmethyl), and 26a (3-methylbutyl) offer 250-fold, 120-fold, and 96-fold selectivity, respectively, for inhibition of AgAChE vs. hAChE. Molecular modeling studies suggests the high species-selectivity of these compounds can be attributed to the greater mobility of the W84 side chain in the choline-binding site of AgAChE, compared to that of W86 in hAChE. Compound 26a has reasonable contact toxicity to G3 strain An. gambiae (LC50 = 269 μg/mL) and low cross-resistance to Akron strain (LC50 = 948 μg/mL), which bears the G119S resistance mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None of the authors have any conflict to report.
Figures
References
-
- World Malaria Report. The World Health Organization; 2016. [last accessed 8/1/17]. available at http://www.who.int/malaria/publications/world-malaria-report-2016/report...
-
- Lindblade KA, Mwandama D, Mzilahowa T, Steinhardt L, Gimnig J, Shah M, Bauleni A, Wong J, Wiegand R, Howell P, Zoya J, Chiphwanya J, Mathanga DP. A cohort study of the effectiveness of insecticide-treated bed nets to prevent malaria in an area of moderate pyrethroid resistance. Malawi, Malaria J. 2015;14:31. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhatt S, Weiss DJ, Cameron E, Bisanzio D, Mappin B, Dalrymple U, Battle KE, Moyes CL, Henry A, Eckhoff PA, Wenger EA, Briet O, Penny MA, Smith TA, Bennett A, Yukich J, Eisele TP, Griffin JT, Fergus CA, Lynch M, Lindgren F, Cohen JM, Murray CLJ, Smith DL, Hay SI, Cibulskis RE, Gething PW. The effect of malaria control on Plasmodium falciparum in Africa between 2000 and 2015. Nature. 2015;526:207–211. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
