Increased Level of Angiopoietin Like Proteins 4 and 8 in People With Sleep Apnea
- PMID: 30524367
- PMCID: PMC6262344
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00651
Increased Level of Angiopoietin Like Proteins 4 and 8 in People With Sleep Apnea
Abstract
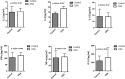
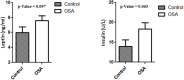
Objective: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a sleep disorder caused by the complete or partial obstruction of the upper airways. The worldwide prevalence of OSA is increasing due to its close association with obesity epidemic and multiple health complications, such as hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and Type 2 diabetes. Angiopoietin-like protein (ANGPTL)-4 and ANGPTL8 (betatrophin) have been suggested to play a role in the development of these diseases through their role in regulating the metabolism of plasma lipid molecules. This study was designed to evaluate ANGPTL4 and 8 levels in an OSA group and a control group to clarify the effect of OSA on ANGPTL4 and 8 levels. Methods: In total, 74 subjects were enrolled in this study, including 22 age- and body mass index (BMI)-matched controls with the Apnea Hypopnea Index (AHI) score of <5 events/h and 52 subjects with an AHI score of >5 events/h. Sleep apnea was assessed using a portable sleep test. ANGPTL4 and 8 levels were measured in plasma samples using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Results: Mean AHI score (2.5 ± 1.6) in the control group was significantly lower than that in the OSA group (22.9 ± 17.9; p < 0.0001). Leptin, interleukin-(IL) 6, insulin, and HOMA-IR values were higher in the OSA group than in the control group. ANGPTL8 level was higher in the OSA group (1130.0 ± 108.61 pg/mL) than in the control group (809.39 ± 108.78 pg/mL; p = 0.041). Similarly, ANGPTL4 was higher in the OSA group (179.26 ± 12.89 ng/mL) than in the control group (142.63 ±7.99 ng/mL; p = 0.018). Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that ANGPTL4 and 8 levels were increased in subjects with OSA, suggesting that the upregulation of these lipid metabolism regulators might play a role in lipid dysregulation observed in people with OSA.
Keywords: ANGPTL4; ANGPTL8; apnea hypopnea index; lipid metabolism; obstructive sleep apnea; polysomnography.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

