Novel Treatments in Lupus
- PMID: 30524430
- PMCID: PMC6262343
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02658
Novel Treatments in Lupus
Abstract
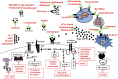
The standard treatment options for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are focused on non-specific immunosuppression. Over the past few years, scientific studies and ongoing clinical trials have shifted the paradigm with rapid advances in developing biologics and small molecules. A number of monoclonal antibodies and small molecule inhibitors have been developed to target specific pathways involved in SLE. Many of these novel therapeutic agents are already being tested in clinical trials and they may 1 day reshape the landscape of SLE treatment. Herein we review potential future therapeutic options for SLE.
Keywords: biologics; clinical trails; lupus; small molecules; treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Furie R, Petri M, Zamani O, Cervera R, Wallace DJ, Tegzova D, et al. . A phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study of belimumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits B lymphocyte stimulator, in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. (2011) 63:3918–30. 10.1002/art.30613 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stohl W, Schwarting A, Okada M, Scheinberg M, Doria A, Hammer AE, et al. . Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous belimumab in systemic lupus erythematosus: a fifty-two-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2017) 69:1016–27. 10.1002/art.40049 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doria A, Stohl W, Schwarting A, Okada M, Scheinberg M, van Vollenhoven R, et al. . Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous belimumab in anti-double-stranded DNA-positive, hypocomplementemic patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2018) 70:1256–64. 10.1002/art.40511 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Isenberg DA, Petri M, Kalunian K, Tanaka Y, Urowitz MB, Hoffman RW, et al. . Efficacy and safety of subcutaneous tabalumab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from ILLUMINATE-1, a 52-week, phase III, multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75:323–31. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207653 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

