Overcoming Endosomal Entrapment in Drug Delivery
- PMID: 30525488
- PMCID: PMC6501178
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.8b00778
Overcoming Endosomal Entrapment in Drug Delivery
Abstract
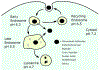
Intracellular delivery of biological agents such as peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids generally rely on the endocytic pathway as the major uptake mechanism, resulting in their entrapment inside the endosome and lysosome. The recent discovery of cell-penetrating molecules of exceptionally high endosomal escape and cytosolic delivery efficiencies and elucidation of their mechanism of action represent major breakthroughs in this field. In this Topical Review, we provide an overview of the recent progress in understanding and enhancing the endosomal escape process and the new opportunities opened up by these recent findings.
Figures

References
-
- Verdine GL, and Walensky LD (2007) The challenge of drugging undruggable targets in cancer: Lessons learned from targeting BCL-2 family members. Clin. Cancer Res 13, 7264–7270. - PubMed
-
- O’Connor TP, and Crystal RG (2006) Genetic medicines: treatment strategies for hereditary disorders. Nat. Rev. Genet 7, 261–276. - PubMed
-
- Scott DE, Bayly AR, Abell C, and Skidmore J (2016) Small molecules, big targets: drug discovery faces the protein-protein interaction challenge. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 15, 533–550. - PubMed
-
- Doudna JA, and Charpentier E (2014) Genome editing. The new frontier of genome engineering with CRISPR-Cas9. Science 346, 1258096. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

