Engineered pH-dependent recycling antibodies enhance elimination of Staphylococcal enterotoxin B superantigen in mice
- PMID: 30526311
- PMCID: PMC6380392
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2018.1545510
Engineered pH-dependent recycling antibodies enhance elimination of Staphylococcal enterotoxin B superantigen in mice
Abstract
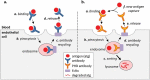
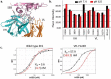
A new modality in antibody engineering has emerged in which the antigen affinity is designed to be pH dependent (PHD). In particular, combining high affinity binding at neutral pH with low affinity binding at acidic pH leads to a novel antibody that can more effectively neutralize the target antigen while avoiding antibody-mediated antigen accumulation. Here, we studied how the in vivo pharmacokinetics of the superantigen, Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB), is affected by an engineered antibody with pH-dependent binding. PHD anti-SEB antibodies were engineered by introducing mutations into a high affinity anti-SEB antibody, 3E2, by rational design and directed evolution. Three antibody mutants engineered in the study have an affinity at pH 6.0 that is up to 68-fold weaker than the control antibody. The pH dependency of each mutant, measured as the pH-dependent affinity ratio (PAR - ratio of affinity at pH 7.4 and pH 6.0), ranged from 6.7-11.5 compared to 1.5 for the control antibody. The antibodies were characterized in mice by measuring their effects on the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics (PK) of SEB after co-administration. All antibodies were effective in neutralizing the toxin and reducing the toxin-induced cytokine production. However, engineered PHD antibodies led to significantly faster elimination of the toxin from the circulation than wild type 3E2. The area under the curve computed from the SEB PK profile correlated well with the PAR value of antibody, indicating the importance of fine tuning the pH dependency of binding. These results suggest that a PHD recycling antibody may be useful to treat intoxication from a bacterial toxin by accelerating its clearance.
Keywords: Staphylococcal enterotoxin B; antigen pharmacokinetics; monoclonal antibody; pH-dependent antibody.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms mediating enhanced neutralization efficacy of staphylococcal enterotoxin B by combinations of monoclonal antibodies.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 13;290(11):6715-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.630715. Epub 2015 Jan 8. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25572397 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a single-chain variable-fragment antibody against the superantigen Staphylococcal enterotoxin B.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 Dec;76(24):8184-91. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01441-10. Epub 2010 Oct 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20952642 Free PMC article.
-
A highly neutralizing human monoclonal antibody targeting a novel linear epitope on staphylococcal enterotoxin B.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2360338. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2360338. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 38857905 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Potent Neutralization of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B In Vivo by Antibodies that Block Binding to the T-Cell Receptor.J Mol Biol. 2019 Oct 4;431(21):4354-4367. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.03.017. Epub 2019 Mar 27. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30928493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody engineering for the development of therapeutic antibodies.Mol Cells. 2005 Aug 31;20(1):17-29. Mol Cells. 2005. PMID: 16258237 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering of pH-dependent antigen binding properties for toxin-targeting IgG1 antibodies using light-chain shuffling.Structure. 2024 Sep 5;32(9):1404-1418.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2024.07.014. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Structure. 2024. PMID: 39146931 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal Antibody Engineering and Design to Modulate FcRn Activities: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 24;23(17):9604. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179604. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequence-based engineering of pH-sensitive antibodies for tumor targeting or endosomal recycling applications.MAbs. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2404064. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2024.2404064. Epub 2024 Sep 17. MAbs. 2024. PMID: 39289783 Free PMC article.
-
A novel sweeping antibody exhibits efficient clearance of the cancer- and autoimmunity-associated cytokine interleukin 16.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 1:2025.07.29.666814. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.29.666814. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40766633 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
An antibody Fc engineered for conditional antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity at the low tumor microenvironment pH.J Biol Chem. 2022 Apr;298(4):101798. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101798. Epub 2022 Mar 3. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35248534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singh S, Kumar NK, Dwiwedi P, Charan J, Kaur R, Sidhu P, Chugh VK Monoclonal Antibodies: A Review. Curr Clin Pharmacol 2018;13:85-99. - PubMed
-
- Igawa T, Ishii S, Tachibana T, Maeda A, Higuchi Y, Shimaoka S, Moriyama C, Watanabe T, Takubo R, Doi Y, et al Antibody recycling by engineered pH-dependent antigen binding improves the duration of antigen neutralization. Nat Biotechnol 2010; 28:1203-7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
