Vasoplegia after implantation of a continuous flow left ventricular assist device: incidence, outcomes and predictors
- PMID: 30526494
- PMCID: PMC6286572
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-018-0645-y
Vasoplegia after implantation of a continuous flow left ventricular assist device: incidence, outcomes and predictors
Abstract
Background: Vasoplegia after routine cardiac surgery is associated with severe postoperative complications and increased mortality. It is also prevalent in patients undergoing implantation of pulsatile flow left ventricular assist devices (LVAD). However, less is known regarding vasoplegia after implantation of newer generations of continuous flow LVADs (cfLVAD). We aim to report the incidence, impact on outcome and predictors of vasoplegia in these patients.
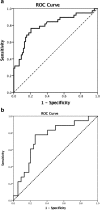
Methods: Adult patients scheduled for primary cfLVAD implantation were enrolled into a derivation cohort (n = 118, 2006-2013) and a temporal validation cohort (n = 73, 2014-2016). Vasoplegia was defined taking into consideration low mean arterial pressure and/or low systemic vascular resistance, preserved cardiac index and high vasopressor support. Vasoplegia was considered after bypass and the first 48 h of ICU stay lasting at least three consecutive hours. This concept of vasoplegia was compared to older definitions reported in the literature in terms of the incidence of postoperative vasoplegia and its association with adverse outcomes. Logistic regression was used to identify independent predictors. Their ability to discriminate patients with vasoplegia was quantified by the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC).
Results: The incidence of vasoplegia was 33.1% using the unified definition of vasoplegia. Vasoplegia was associated with increased ICU length-of-stay (10.5 [6.9-20.8] vs 6.1 [4.6-10.4] p = 0.002), increased ICU-mortality (OR 5.8, 95% CI 1.9-18.2) and one-year-mortality (OR 3.9, 95% CI 1.5-10.2), and a higher incidence of renal failure (OR 4.3, 95% CI 1.8-10.4). Multivariable analysis identified previous cardiothoracic surgery, preoperative dopamine administration, preoperative bilirubin levels and preoperative creatinine clearance as independent preoperative predictors of vasoplegia. The resultant prediction model exhibited a good discriminative ability (AUC 0.80, 95% CI 0.71-0.89, p < 0.01). Temporal validation resulted in an AUC of 0.74 (95% CI 0.61-0.87, p < 0.01).
Conclusions: In the era of the new generation of cfLVADs, vasoplegia remains a prevalent (33%) and critical condition with worse short-term outcomes and survival. We identified previous cardiothoracic surgery, preoperative treatment with dopamine, preoperative bilirubin levels and preoperative creatinine clearance as independent predictors.
Keywords: Cardiac Vasoplegia syndrome; Incidence; Mechanical circulatory support; Morbidity; Mortality; Outcome; Prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was performed in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki. Prior to data collection the study protocol was assessed by the institutional review board of the University Medical Centre Utrecht, The Netherlands and approved with an exemption from requiring ethical approval (14–053/C) because patients were not subjected to any investigational action.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Argenziano M, Chen JM, Choudri AF, Cullinane S, Garfein E, Weinberg AD, et al. Management of vasodilatory shock after cardiac surgery: identification of predisposing factors and use of a novel pressor agent. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1998;116:973–980. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5223(98)70049-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Papadopoulos G, Sintou E, Siminelakis S, Koletsis E, Baikoussis NG, Apostolakis E. Perioperative infusion of low- dose of vasopressin for prevention and management of vasodilatory vasoplegic syndrome in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting-a double-blind randomized study. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2010;5:17. doi: 10.1186/1749-8090-5-17. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

