Inhibition of Inflammatory Signaling in Tet2 Mutant Preleukemic Cells Mitigates Stress-Induced Abnormalities and Clonal Hematopoiesis
- PMID: 30526882
- PMCID: PMC6317370
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.10.013
Inhibition of Inflammatory Signaling in Tet2 Mutant Preleukemic Cells Mitigates Stress-Induced Abnormalities and Clonal Hematopoiesis
Abstract
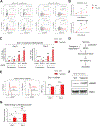
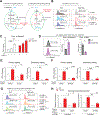
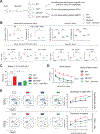
Inflammation is a risk factor for cancer development. Individuals with preleukemic TET2 mutations manifest clonal hematopoiesis and are at a higher risk of developing leukemia. How inflammatory signals influence the survival of preleukemic hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) is unclear. We show a rapid increase in the frequency and absolute number of Tet2-KO mature myeloid cells and HSPCs in response to inflammatory stress, which results in enhanced production of inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-6 (IL-6), and resistance to apoptosis. IL-6 induces hyperactivation of the Shp2-Stat3 signaling axis, resulting in increased expression of a novel anti-apoptotic long non-coding RNA (lncRNAs), Morrbid, in Tet2-KO myeloid cells and HSPCs. Expression of activated Shp2 in HSPCs phenocopies Tet2 loss with regard to hyperactivation of Stat3 and Morrbid. In vivo, pharmacologic inhibition of Shp2 or Stat3 or genetic loss of Morrbid in Tet2 mutant mice rescues inflammatory-stress-induced abnormalities in HSPCs and mature myeloid cells, including clonal hematopoiesis.
Keywords: Morrbid; Tet2; inflammation; preleukemic; stem cells.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
Dr. Mark R. Kelley has licensed E3330 (APX3330) through Indiana University Research and Technology Corporation to Apexian Pharmaceuticals. Apexian Pharmaceuticals had neither control nor oversight of the studies, interpretation, or presentation of the data in this manuscript. Morvarid Mohseni is an employee of Novartis Institutes of Biomedical Research. Other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Abegunde SO, Buckstein R, Wells RA, and Rauh MJ (2018). An inflammatory environment containing TNFalpha favors Tet2 mutant clonal hematopoiesis. Experimental Hematology 59, 60–65. - PubMed
-
- Abkowitz JL (2014). Clone Wars — The Emergence of Neoplastic Blood-Cell Clones with Aging. New England Journal of Medicine 371, 2523–2525. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein CN, Blanchard JF, Kliewer E, and Wajda A (2001). Cancer risk in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Cancer 91, 854–862. - PubMed
-
- Bouillet P, Metcalf D, Huang DC, Tarlinton DM, Kay TW, Kontgen F, Adams JM, and Strasser A (1999). Proapoptotic Bcl-2 relative Bim required for certain apoptotic responses, leukocyte homeostasis, and to preclude autoimmunity. Science 286, 1735–1738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

