Hypoxia: A breath of fresh air for the meibomian gland
- PMID: 30528291
- PMCID: PMC6529253
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtos.2018.12.001
Hypoxia: A breath of fresh air for the meibomian gland
Abstract
Purpose: Optimal meibomian gland (MG) function is critically important for the health and wellbeing of the ocular surface. We hypothesize that low oxygen (O2) conditions promote the function of human MG epithelial cells (HMGECs) and that human MGs exist in a relatively hypoxic environment. The purpose of this study was to test our hypotheses.
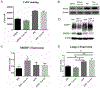
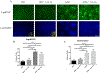
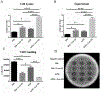
Methods: We used human and mouse eyelid segments, and immortalized human MG epithelial cells (IHMGECs) in our studies. To evaluate oxygen (O2) levels in the mouse MG and vicinity, we injected pimonidazole (pimo), a hypoxia marker, before sacrifice. Human eyelid samples were stained with the hypoxia marker glucose transporter 1 (Glut-1). To determine the effect of low O2 levels on IHMGECs, we cultured cells under proliferating and differentiating conditions in both normoxic (21% O2) and hypoxic (3% O2) conditions for 5-15 days. IHMGECs were evaluated for cell number, neutral lipid content, lysosome accumulation, expression of biomarker proteins and DNase II activity.
Results: Our results demonstrate that human and mouse MGs, but not the surrounding connective tissue, exist in a relatively hypoxic environment in vivo. In addition, our findings show that hypoxia does not influence IHMGEC numbers in basal or proliferating culture conditions, but does stimulate the expression of SREBP-1 in differentiating IHMGECs. Hypoxia also significantly increased DNase II activity, and apparently IHMGEC terminal differentiation.
Conclusions: Our Results support our hypotheses, and indicate that relative hypoxia promotes MG function.
Keywords: DNase II; Glucose transporter 1; Hypoxia; Meibomian gland; Pimonidazole.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Green-Church KB, Butovich I, Willcox M, Borchman D, Paulsen F, Barabino S, et al. The international workshop on meibomian gland dysfunction: report of the subcommittee on tear film lipids and lipid-protein interactions in health and disease. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science. 2011;52:1979–93. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bron AJ, Tiffany JM. The contribution of meibomian disease to dry eye. The ocular surface. 2004;2:149–65. - PubMed
-
- Bron AJ, Tiffany JM, Gouveia SM, Yokoi N, Voon LW. Functional aspects of the tear film lipid layer. Experimental eye research. 2004;78:347–60. - PubMed
-
- McCulley JP, Shine WE. Meibomian gland function and the tear lipid layer. The ocular surface. 2003;1:97–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

