Installation of a cancer promoting WNT/SIX1 signaling axis by the oncofusion protein MLL-AF9
- PMID: 30528456
- PMCID: PMC6354558
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.11.039
Installation of a cancer promoting WNT/SIX1 signaling axis by the oncofusion protein MLL-AF9
Abstract
Background: Chromosomal translocation-induced expression of the chromatin modifying oncofusion protein MLL-AF9 promotes acute myelocytic leukemia (AML). Whereas WNT/β-catenin signaling has previously been shown to support MLL-AF9-driven leukemogenesis, the mechanism underlying this relationship remains unclear.
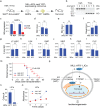
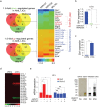
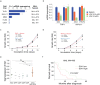
Methods: We used two novel small molecules targeting WNT signaling as well as a genetically modified mouse model that allow targeted deletion of the WNT protein chaperone Wntless (WLS) to evaluate the role of WNT signaling in AML progression. ATAC-seq and transcriptome profiling were deployed to understand the cellular consequences of disrupting a WNT signaling in leukemic initiating cells (LICs).
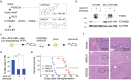
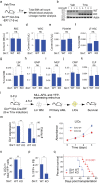
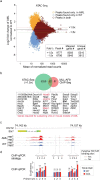
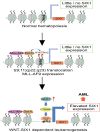
Findings: We identified Six1 to be a WNT-controlled target gene in MLL-AF9-transformed leukemic initiating cells (LICs). MLL-AF9 alters the accessibility of Six1 DNA to the transcriptional effector TCF7L2, a transducer of WNT/β-catenin gene expression changes. Disruption of WNT/SIX1 signaling using inhibitors of the Wnt signaling delays the development of AML.
Interpretation: By rendering TCF/LEF-binding elements controlling Six1 accessible to TCF7L2, MLL-AF9 promotes WNT/β-catenin-dependent growth of LICs. Small molecules disrupting WNT/β-catenin signaling block Six1 expression thereby disrupting leukemia driven by MLL fusion proteins.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Six1 regulates leukemia stem cell maintenance in acute myeloid leukemia.Cancer Sci. 2019 Jul;110(7):2200-2210. doi: 10.1111/cas.14033. Epub 2019 May 29. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 31050834 Free PMC article.
-
ZNF521 Enhances MLL-AF9-Dependent Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transformation in Acute Myeloid Leukemias by Altering the Gene Expression Landscape.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 6;22(19):10814. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910814. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639154 Free PMC article.
-
The AAA+ ATPase RUVBL2 is a critical mediator of MLL-AF9 oncogenesis.Leukemia. 2013 Jul;27(7):1461-8. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.42. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Leukemia. 2013. PMID: 23403462
-
Learning from mouse models of MLL fusion gene-driven acute leukemia.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020 Aug;1863(8):194550. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194550. Epub 2020 Apr 19. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020. PMID: 32320749 Review.
-
Polycomb complexes in MLL-AF9-related leukemias.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2022 Aug;75:101920. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2022.101920. Epub 2022 May 21. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2022. PMID: 35609423 Review.
Cited by
-
BCOR Binding to MLL-AF9 Is Essential for Leukemia via Altered EYA1, SIX, and MYC Activity.Blood Cancer Discov. 2020 Sep;1(2):162-177. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-20-0036. Blood Cancer Discov. 2020. PMID: 32954361 Free PMC article.
-
The PAX-SIX-EYA-DACH network modulates GATA-FOG function in fly hematopoiesis and human erythropoiesis.Development. 2020 Jan 3;147(1):dev177022. doi: 10.1242/dev.177022. Development. 2020. PMID: 31806659 Free PMC article.
-
A Box of Chemistry to Inhibit the MEN1 Tumor Suppressor Gene Promoting Leukemia.ChemMedChem. 2021 May 6;16(9):1391-1402. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202000972. Epub 2021 Mar 10. ChemMedChem. 2021. PMID: 33534953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt Signaling in Leukemia and Its Bone Marrow Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 28;21(17):6247. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176247. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32872365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NKL Homeobox Genes NKX2-3 and NKX2-4 Deregulate Megakaryocytic-Erythroid Cell Differentiation in AML.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 22;22(21):11434. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111434. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768865 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

