Merged plantarflexor muscle activity is predictive of poor walking performance in post-stroke hemiparetic subjects
- PMID: 30528553
- PMCID: PMC6310645
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2018.11.011
Merged plantarflexor muscle activity is predictive of poor walking performance in post-stroke hemiparetic subjects
Abstract
Stroke is the leading cause of long-term disability and individuals post-stroke often experience impaired walking ability. The plantarflexor (PF) muscles are critical to walking through their contributions to the ground reaction forces and body segment energetics. Previous studies have shown muscle activity during walking can be grouped into co-excited muscle sets, or modules. Improper co-activation, or merging of modules, is a common impairment in individuals post-stroke. The purpose of this study was to determine the influence of merged PF modules on walking performance in individuals post stroke by examining balance control, body support and propulsion, and walking symmetry. Muscle modules were identified using non-negative matrix factorization to classify subjects as having an independent or merged PF module. The merged group had decreased balance control with a significantly higher frontal plane whole-body angular momentum than both the independent and control groups, while the independent and control groups were not significantly different. The merged group also had higher paretic braking and nonparetic propulsion than both the independent and control groups. These results remained when comparisons were limited to subjects who had the same number of modules, indicating this was not a general effect due to subjects with merged PF having fewer modules. It is likely that a merged PF module is indicative of general PF dysfunction even when some activation occurs at the appropriate time. These results suggest an independent PF module is critical to walking performance, and thus obtaining an independent PF module should be a crucial aim of stroke rehabilitation.
Keywords: Biomechanics; Gait; Muscle modules; Rehabilitation; Synergies.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
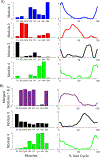
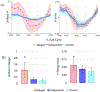
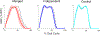
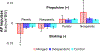
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Das SR, Deo R, de Ferranti SD, Floyd J, Fornage M, Gillespie C, Isasi CR, Jiménez MC, Jordan LC, Judd SE, Lackland D, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth L, Liu S, Longenecker CT, Mackey RH, Matsushita K, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, Neumar RW, Palaniappan L, Pandey DK, Thiagarajan RR, Reeves MJ, Ritchey M, Rodriguez CJ, Roth GA, Rosamond WD, Sasson C, Towfighi A, Tsao CW, Turner MB, Virani SS, Voeks JH, Willey JZ, Wilkins JT, Wu JH, Alger HM, Wong SS, Muntner P, American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee, 2017. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 135, e146–e603. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000485 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

