The imminent epidemic of atrial fibrillation and its concomitant diseases - Myocardial infarction and heart failure - A cause for concern
- PMID: 30528622
- PMCID: PMC6524760
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.11.123
The imminent epidemic of atrial fibrillation and its concomitant diseases - Myocardial infarction and heart failure - A cause for concern
Abstract
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is increasingly common in the general population. It often coincides with myocardial infarction (MI) and heart failure (HF) which are also diseases in older adults. All three conditions share common cardiovascular risk factors. While hypertension and obesity are central risk factors for all three diseases, smoking and diabetes appear to have less impact on AF. To date, age is the single most important risk factor for AF in the general population. Further, epidemiological studies suggest a strong association of AF to MI and HF. The underlying pathophysiological mechanisms are complex and not fully understood. Both MI and HF can trigger development of AF, mainly by promoting structural and electrical atrial remodeling. On the other hand, AF facilitates HF and MI development via multiple mechanisms, resulting in a vicious circle of cardiac impairment and adverse cardiovascular prognosis. Consequently, to prevent and treat the coincidence of AF and HF or MI a strict optimization of cardiovascular risk factors is required.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Cardiovascular risk factors; Epidemiology; Heart failure; Myocardial infarction; Population-attributable risk.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
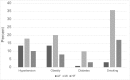
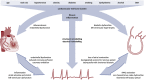
References
-
- Abed H.S., Samuel C.S., Lau D.H., Kelly D.J., Royce S.G., Alasady M., Mahajan R., Kuklik P., Zhang Y., Brooks A.G., Nelson A.J., Worthley S.G., Abhayaratna W.P., Kalman J.M., Wittert G.A., Sanders P. Obesity results in progressive atrial structural and electrical remodeling: implications for atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2013;10:90–100. - PubMed
-
- Pathak R.K., Middeldorp M.E., Lau D.H., Mehta A.B., Mahajan R., Twomey D., Alasady M., Hanley L., Antic N.A., McEvoy R.D., Kalman J.M., Abhayaratna W.P., Sanders P. Aggressive risk factor reduction study for atrial fibrillation and implications for the outcome of ablation: the ARREST-AF cohort study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014;64:2222–2231. - PubMed
-
- Anand S.S., Islam S., Rosengren A., Franzosi M.G., Steyn K., Yusufali A.H., Keltai M., Diaz R., Rangarajan S., Yusuf S. Risk factors for myocardial infarction in women and men: insights from the INTERHEART study. Eur. Heart J. 2008;29:932–940. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S., Hawken S., Ôunpuu S., Dans T., Avezum A., Lanas F., McQueen M., Budaj A., Pais P., Varigos J., Lisheng L. Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries in a case-control study based on the INTERHEART study. Lancet. 2004;364:937–952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

