Dual inhibition of Kif15 by oxindole and quinazolinedione chemical probes
- PMID: 30528696
- PMCID: PMC6681659
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.12.008
Dual inhibition of Kif15 by oxindole and quinazolinedione chemical probes
Abstract
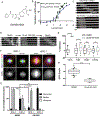
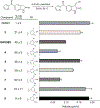
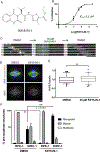
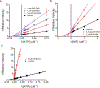
The mitotic spindle is a microtubule-based machine that segregates a replicated set of chromosomes during cell division. Many cancer drugs alter or disrupt the microtubules that form the mitotic spindle. Microtubule-dependent molecular motors that function during mitosis are logical alternative mitotic targets for drug development. Eg5 (Kinesin-5) and Kif15 (Kinesin-12), in particular, are an attractive pair of motor proteins, as they work in concert to drive centrosome separation and promote spindle bipolarity. Furthermore, we hypothesize that the clinical failure of Eg5 inhibitors may be (in part) due to compensation by Kif15. In order to test this idea, we screened a small library of kinase inhibitors and identified GW108X, an oxindole that inhibits Kif15 in vitro. We show that GW108X has a distinct mechanism of action compared with a commercially available Kif15 inhibitor, Kif15-IN-1 and may serve as a lead with which to further develop Kif15 inhibitors as clinically relevant agents.
Keywords: Eg5; Kif15; Kinesin; Mitosis; Oxindole.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Huang TC; Campbell TC, Comparison of weekly versus every 3 weeks paclitaxel in the treatment of advanced solid tumors: a meta-analysis. Cancer Treat Rev 2012, 38 (6), 613–7. - PubMed
-
- Ferrier J; Pereira V; Busserolles J; Authier N; Balayssac D, Emerging trends in understanding chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2013, 17 (10), 364. - PubMed
-
- Dominguez-Brauer C; Thu KL; Mason JM; Blaser H; Bray MR; Mak TW, Targeting Mitosis in Cancer: Emerging Strategies. Mol Cell 2015, 60 (4), 524–36. - PubMed
-
- Mayer TU; Kapoor TM; Haggarty SJ; King RW; Schreiber SL; Mitchison TJ, Small molecule inhibitor of mitotic spindle bipolarity identified in a phenotype-based screen. Science 1999, 286 (5441), 971–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

