Assessing the Association Between GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Use and Diabetic Retinopathy Through the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System
- PMID: 30530488
- PMCID: PMC6341287
- DOI: 10.2337/dc18-1893
Assessing the Association Between GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Use and Diabetic Retinopathy Through the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System
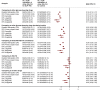
Figures
References
-
- Fan Y, Liu K, Wang Q, Ruan Y, Ye W, Zhang Y. Exendin-4 alleviates retinal vascular leakage by protecting the blood-retinal barrier and reducing retinal vascular permeability in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Exp Eye Res 2014;127:104–116 - PubMed
-
- Simó R, Hernández C. GLP-1R as a target for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy: friend or foe? Diabetes 2017;66:1453–1460 - PubMed
-
- Hernández C, Bogdanov P, Corraliza L, et al. . Topical administration of GLP-1 receptor agonists prevents retinal neurodegeneration in experimental diabetes. Diabetes 2016;65:172–187 - PubMed