cAMP-dependent activation of the Rac guanine exchange factor P-REX1 by type I protein kinase A (PKA) regulatory subunits
- PMID: 30530493
- PMCID: PMC6378977
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006691
cAMP-dependent activation of the Rac guanine exchange factor P-REX1 by type I protein kinase A (PKA) regulatory subunits
Abstract
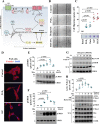
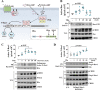
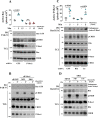
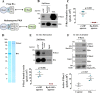
Regulatory subunits of protein kinase A (PKA) inhibit its kinase subunits. Intriguingly, their potential as cAMP-dependent signal transducers remains uncharacterized. We recently reported that type I PKA regulatory subunits (RIα) interact with phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent Rac exchange factor 1 (P-REX1), a chemotactic Rac guanine exchange factor (RacGEF). Because P-REX1 is known to be phosphorylated and inhibited by PKA, its interaction with RIα suggests that PKA regulatory and catalytic subunits may fine-tune P-REX1 activity or those of its target pools. Here, we tested whether RIα acts as a cAMP-dependent factor promoting P-REX1-mediated Rac activation and cell migration. We observed that Gs-coupled EP2 receptors indeed promote endothelial cell migration via RIα-activated P-REX1. Expression of the P-REX1-PDZ1 domain prevented RIα/P-REX1 interaction, P-REX1 activation, and EP2-dependent cell migration, and P-REX1 silencing abrogated RIα-dependent Rac activation. RIα-specific cAMP analogs activated P-REX1, but lost this activity in RIα-knockdown cells, and cAMP pulldown assays revealed that P-REX1 preferentially interacts with free RIα. Moreover, purified RIα directly activated P-REX1 in vitro We also found that the RIα CNB-B domain is critical for the interaction with P-REX1, which was increased in RIα mutants, such as the acrodysostosis-associated mutant, that activate P-REX1 at basal cAMP levels. RIα and Cα PKA subunits targeted distinct P-REX1 molecules, indicated by an absence of phosphorylation in the active fraction of P-REX1. This was in contrast to the inactive fraction in which phosphorylated P-REX1 was present, suggesting co-existence of dual stimulatory and inhibitory effects. We conclude that PKA's regulatory subunits are cAMP-dependent signal transducers.
Keywords: EP2 receptors; G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR); P-REX1; Rac (Rac GTPase); Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (RhoGEF); cell migration; cell signaling; chemotaxis; cyclic AMP (cAMP); endothelial cell; guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF); heterotrimeric G protein; protein kinase A (PKA); regulatory subunit alpha (RIα); wound healing.
© 2019 Adame-García et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protein Kinase A (PKA) Type I Interacts with P-Rex1, a Rac Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor: EFFECT ON PKA LOCALIZATION AND P-Rex1 SIGNALING.J Biol Chem. 2016 Mar 18;291(12):6182-99. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.712216. Epub 2016 Jan 21. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26797121 Free PMC article.
-
Gβγ signaling to the chemotactic effector P-REX1 and mammalian cell migration is directly regulated by Gαq and Gα13 proteins.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jan 11;294(2):531-546. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006254. Epub 2018 Nov 16. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30446620 Free PMC article.
-
"A-kinase" regulator runs amok to provide a paradigm shift in cAMP signaling.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 15;294(7):2247-2248. doi: 10.1074/jbc.H119.007622. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30765510 Free PMC article.
-
The Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor P-Rex1 as a potential drug target for cancer metastasis and inflammatory diseases.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Mar;153:104676. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104676. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32006571 Review.
-
Chemoprevention with protein kinase A RIalpha antisense in DMBA-mammary carcinogenesis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Nov;1058:255-64. doi: 10.1196/annals.1359.038. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 16394142 Review.
Cited by
-
P-Rex1 Signaling Hub in Lower Grade Glioma Patients, Found by In Silico Data Mining, Correlates With Reduced Survival and Augmented Immune Tumor Microenvironment.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 7;12:922025. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.922025. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35875157 Free PMC article.
-
Gαs directly drives PDZ-RhoGEF signaling to Cdc42.J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 11;295(50):16920-16928. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AC120.015204. Epub 2020 Oct 6. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33023908 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding P-Rex regulation: structural breakthroughs and emerging perspectives.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Aug 28;52(4):1849-1860. doi: 10.1042/BST20231546. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 39023851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P-Rex1 Controls Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor Signalling, Morphology, and Cell-Cycle Progression in Neuronal Cells.Cells. 2021 Sep 18;10(9):2474. doi: 10.3390/cells10092474. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572121 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoproteomic Analysis as an Approach for Understanding Molecular Mechanisms of cAMP-Dependent Actions.Mol Pharmacol. 2021 May;99(5):342-357. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.120.000197. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Mol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33574048 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

