Peroxisome biogenesis, membrane contact sites, and quality control
- PMID: 30530632
- PMCID: PMC6322382
- DOI: 10.15252/embr.201846864
Peroxisome biogenesis, membrane contact sites, and quality control
Abstract
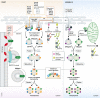
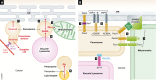
Peroxisomes are conserved organelles of eukaryotic cells with important roles in cellular metabolism, human health, redox homeostasis, as well as intracellular metabolite transfer and signaling. We review here the current status of the different co-existing modes of biogenesis of peroxisomal membrane proteins demonstrating the fascinating adaptability in their targeting and sorting pathways. While earlier studies focused on peroxisomes as autonomous organelles, the necessity of the ER and potentially even mitochondria as sources of peroxisomal membrane proteins and lipids has come to light in recent years. Additionally, the intimate physical juxtaposition of peroxisomes with other organelles has transitioned from being viewed as random encounters to a growing appreciation of the expanding roles of such inter-organellar membrane contact sites in metabolic and regulatory functions. Peroxisomal quality control mechanisms have also come of age with a variety of mechanisms operating both during biogenesis and in the cellular response to environmental cues.
Keywords: de novo peroxisome biogenesis; peroxisomal membrane contact sites; peroxisomal membrane protein biogenesis; peroxisome growth and division; peroxisome quality control.
© 2018 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Tabak HF, Braakman I, Distel B (1999) Peroxisomes: simple in function but complex in maintenance. Trends Cell Biol 9: 447–453 - PubMed
-
- Waterham HR, Ferdinandusse S, Wanders RJ (2016) Human disorders of peroxisome metabolism and biogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1863: 922–933 - PubMed
-
- Honsho M, Yamashita S, Fujiki Y (2016) Peroxisome homeostasis: mechanisms of division and selective degradation of peroxisomes in mammals. Biochim Biophys Acta 1863: 984–991 - PubMed

