Predator stress-induced depression is associated with inhibition of hippocampal neurogenesis in adult male mice
- PMID: 30531013
- PMCID: PMC6301170
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.244792
Predator stress-induced depression is associated with inhibition of hippocampal neurogenesis in adult male mice
Abstract
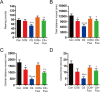
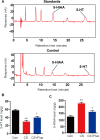
Stress has been suggested to disturb the 5-hydroxytryptamine system and decrease neurogenesis, which contribute to the development of depression. Few studies have investigated the effect of predator stress, a type of psychological stress, on depression and hippocampal neurogenesis in adult mice; we therefore investigated this in the present study. A total of 35 adult male Kunming mice were allocated to a cat stress group, cat odor stress group, cat stress + fluoxetine group, cat odor stress + fluoxetine group, or a control group (no stress/treatment). After 12 days of cat stress or cat odor stress, behavioral correlates of depression were measured using the open field test, elevated plus maze test, and dark-avoidance test. The concentrations of hippocampal 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid were measured using high-performance liquid chromatography-electrochemical detection. Neurogenesis was also analyzed using a bromodeoxyuridine and doublecortin double-immunostaining method. Cat stress and cat odor stress induced depression-like behaviors; this effect was stronger in the cat stress model. Furthermore, compared with the control group, cat stress mice exhibited lower 5-hydroxytryptamine concentrations, higher 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid concentrations, and significantly fewer bromodeoxyuridine+/doublecortin+-labeled cells in the dentate gyrus, which was indicative of less neurogenesis. The changes observed in the cat stress group were not seen in the cat stress + fluoxetine group, which suggests that the effects of predator stress on depression and neurogenesis were reversed by fluoxetine. Taken together, our results indicate that depression-like behaviors induced by predator stress are associated with the inhibition of hippocampal neurogenesis.
Keywords: 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid; 5-hydroxytryptamine; behavioral evaluation; cat odor stress; cat stress; dark-avoidance test; depressive disorder; elevated plus maze test; hippocampal neurogenesis; nerve regeneration; neural regeneration; open field test.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures



References
-
- Airan RD, Meltzer LA, Roy M, Gong Y, Chen H, Deisseroth K. High-speed imaging reveals neurophysiological links to behavior in an animal model of depression. Science. 2007;317:819–823. - PubMed
-
- Apfelbach R, Blanchard CD, Blanchard RJ, Hayes RA, McGregor IS. The effects of predator odors in mammalian prey species: a review of field and laboratory studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2005;29:1123–1144. - PubMed
-
- Bourin M, Hascoët M. The mouse light/dark box test. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;463:55–65. - PubMed
-
- Brezun JM, Daszuta A. Serotonin may stimulate granule cell proliferation in the adult hippocampus, as observed in rats grafted with foetal raphe neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;12:391–396. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

