YAP1-induced MALAT1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis by sponging miR-126-5p in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 30531836
- PMCID: PMC6484768
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-018-0628-y
YAP1-induced MALAT1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis by sponging miR-126-5p in colorectal cancer
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: YAP1-induced MALAT1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis by sponging miR-126-5p in colorectal cancer.Oncogene. 2023 Aug;42(35):2657. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02794-4. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 37507527 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
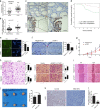
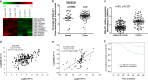
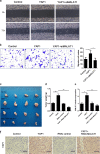
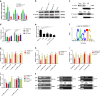
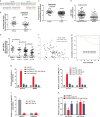
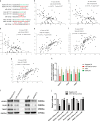
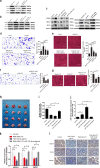
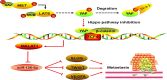
Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) exerts significant effects in various malignancies. However, the oncogenic role of YAP1 remains controversial, and the mechanism by which YAP1 regulates non-coding RNAs is still largely unknown. The present study aimed to assess the effect of YAP1 on the malignant behaviors of colorectal carcinoma (CRC) and explore the underlying regulatory mechanism of the YAP1-MALAT1-miR-126-5p axis. YAP1 was highly expressed in CRC tissues as assessed by GSE20916 and its expression was negatively correlated with overall survival in 83 CRC cases. Meanwhile, YAP1 promoted proliferation, invasion, and migration in colon cancer cells, in vitro and in vivo. MALAT1 was obviously expressed, with differential expression of 11 lncRNAs in HCT116 cells after transfection with siYAP1 or si-Ctl. Based on bioinformatics prediction, immunoprecipitation (IP), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), the interaction of YAP1 with TCF4/β-catenin was regulated by MALAT1. Bioinformatics prediction, dual luciferase assay, RNA-IP, and RNA pull-down assay demonstrated that YAP1-induced MALAT1 promoted the expression of metastasis-associated molecules such as VEGFA, SLUG, and TWIST, by sponging miR-126-5p in CRC. These findings indicated that the YAP1-MALAT1-miR-126-5p axis could control angiogenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in CRC, providing potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for CRC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

