Resistance to Src inhibition alters the BRAF-mutant tumor secretome to promote an invasive phenotype and therapeutic escape through a FAK>p130Cas>c-Jun signaling axis
- PMID: 30531837
- PMCID: PMC6450711
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-018-0617-1
Resistance to Src inhibition alters the BRAF-mutant tumor secretome to promote an invasive phenotype and therapeutic escape through a FAK>p130Cas>c-Jun signaling axis
Abstract
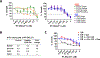
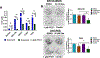
Few therapy options exist for patients with advanced papillary and anaplastic thyroid cancer. We and others have previously identified c-Src as a key mediator of thyroid cancer pro-tumorigenic processes and a promising therapeutic target for thyroid cancer. To increase the efficacy of targeting Src in the clinic, we sought to define mechanisms of resistance to the Src inhibitor, dasatinib, to identify key pathways to target in combination. Using a panel of thyroid cancer cell lines expressing clinically relevant mutations in BRAF or RAS, which were previously developed to be resistant to dasatinib, we identified a switch to a more invasive phenotype in the BRAF-mutant cells as a potential therapy escape mechanism. This phenotype switch is driven by FAK kinase activity, and signaling through the p130Cas>c-Jun signaling axis. We have further shown this more invasive phenotype is accompanied by alterations in the secretome through the increased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, and the pro-invasive metalloprotease, MMP-9. Furthermore, IL-1β signals via a feedforward autocrine loop to promote invasion through a FAK>p130Cas>c-Jun>MMP-9 signaling axis. We further demonstrate that upfront combined inhibition of FAK and Src synergistically inhibits growth and invasion, and induces apoptosis in a panel of BRAF- and RAS-mutant thyroid cancer cell lines. Together our data demonstrate that acquired resistance to single-agent Src inhibition promotes a more invasive phenotype through an IL-1β>FAK>p130Cas>c-Jun >MMP signaling axis, and that combined inhibition of FAK and Src has the potential to block this inhibitor-induced phenotype switch.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
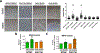
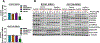
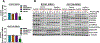
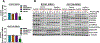


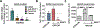



Similar articles
-
The Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway Facilitates Resistance to the Src Inhibitor Dasatinib in Thyroid Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Aug;15(8):1952-63. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0702. Epub 2016 May 24. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27222538 Free PMC article.
-
p63 drives invasion in keratinocytes expressing HPV16 E6/E7 genes through regulation of Src-FAK signalling.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 7;8(10):16202-16219. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3892. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 26001294 Free PMC article.
-
TGFβ induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition of thyroid cancer cells by both the BRAF/MEK/ERK and Src/FAK pathways.Mol Carcinog. 2016 Nov;55(11):1639-1654. doi: 10.1002/mc.22415. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Mol Carcinog. 2016. PMID: 26392228
-
Clinical Development of BRAF plus MEK Inhibitor Combinations.Trends Cancer. 2020 Sep;6(9):797-810. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.05.009. Epub 2020 Jun 13. Trends Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32540454 Review.
-
Targeting the complexity of Src signalling in the tumour microenvironment of pancreatic cancer: from mechanism to therapy.FEBS J. 2019 Sep;286(18):3510-3539. doi: 10.1111/febs.15011. Epub 2019 Aug 5. FEBS J. 2019. PMID: 31330086 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Secretome Screening of BRAFV600E-Mutated Colon Cancer Cells Resistant to Vemurafenib.Biology (Basel). 2023 Apr 17;12(4):608. doi: 10.3390/biology12040608. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37106808 Free PMC article.
-
Focal Adhesion Kinase Provides a Collateral Vulnerability That Can Be Leveraged to Improve mTORC1 Inhibitor Efficacy.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 11;14(14):3374. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143374. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884439 Free PMC article.
-
Focal adhesion kinase signaling - tumor vulnerabilities and clinical opportunities.J Cell Sci. 2024 Jul 15;137(14):jcs261723. doi: 10.1242/jcs.261723. Epub 2024 Jul 22. J Cell Sci. 2024. PMID: 39034922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of NIS Plasma Membrane Interactors Discloses Key Regulation by a SRC/RAC1/PAK1/PIP5K/EZRIN Pathway with Potential Implications for Radioiodine Re-Sensitization Therapy in Thyroid Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 30;13(21):5460. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215460. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771624 Free PMC article.
-
BCAR1 promotes proliferation and cell growth in lung adenocarcinoma via upregulation of POLR2A.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Nov;11(11):3326-3336. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13676. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33001583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carneiro RM, Carneiro BA, Agulnik M, Kopp PA, Giles FJ. Targeted therapies in advanced differentiated thyroid cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2015; - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

