The lung microenvironment: an important regulator of tumour growth and metastasis
- PMID: 30532012
- PMCID: PMC6749995
- DOI: 10.1038/s41568-018-0081-9
The lung microenvironment: an important regulator of tumour growth and metastasis
Abstract
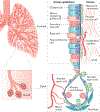
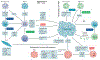
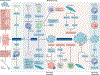
Lung cancer is a major global health problem, as it is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Major advances in the identification of key mutational alterations have led to the development of molecularly targeted therapies, whose efficacy has been limited by emergence of resistance mechanisms. US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved therapies targeting angiogenesis and more recently immune checkpoints have reinvigorated enthusiasm in elucidating the prognostic and pathophysiological roles of the tumour microenvironment in lung cancer. In this Review, we highlight recent advances and emerging concepts for how the tumour-reprogrammed lung microenvironment promotes both primary lung tumours and lung metastasis from extrapulmonary neoplasms by contributing to inflammation, angiogenesis, immune modulation and response to therapies. We also discuss the potential of understanding tumour microenvironmental processes to identify biomarkers of clinical utility and to develop novel targeted therapies against lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD & Jemal A Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 68, 7–30 (2018). - PubMed
-
-
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D & Boshoff C The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 553, 446–454 (2018).
This review highlights recent progress in lung cancer biology and therapeutic strategies that are impacting outcomes for patients with advanced-stage NSCLC.
-
-
- Mayekar MK & Bivona TG Current landscape of targeted therapy in lung cancer. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 102, 757–764 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Jamal-Hanjani M et al. Tracking the evolution of non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 376, 2109–2121 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

