Antithrombotic effects and related mechanisms of Salvia deserta Schang root EtOAc extracts
- PMID: 30532017
- PMCID: PMC6288089
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-36026-7
Antithrombotic effects and related mechanisms of Salvia deserta Schang root EtOAc extracts
Abstract
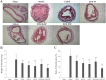
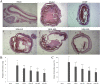
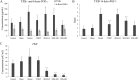
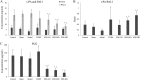
Salvia deserta Schang (SDS) belongs to the same family as Salvia miltiorrhiza bunge, one of the antithrombotic Chinese herbal medicines. In our study, EtOAc root extracts were analyzed for their effects on adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-induced platelet aggregation in rabbits and FeCl3-induced rat common carotid artery thrombosis as well as on rat blood plasma concentrations of thromboxane B2 (TXB2), 6-keto-prostaglandin F1 alpha (6-keto-PGF1α), antithrombin-III (AT-III), protein C (PC), plasminogen (PLG), plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1), von Willebrand factor (vWF) and tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA). EtOAc extracts from SDS roots had significant inhibitory effects on ADP-induced maximum platelet aggregation rate (10.2 ± 2.6 vs control 35.7 ± 5.2; P < 0.05), reduced the FeCl3-induced rat common carotid artery thrombus weight and thrombus area ratio (P < 0.05), significantly decreased plasma TXB2, vWF and PAI-1 levels and increased 6-keto-PGF1α and t-PA levels in a dose dependent manner (all P < 0.05). Thus, the ratio of TXB2/6-keto-PGF1α was significantly decreased (P < 0.05), while the ratio of t-PA/PAI-1 was significantly increased (P < 0.05). In addition, enhanced AT-III and PC activities indicated coagulation inactivation effects of EtOAc SDS root extracts. EtOAc extraction from SDS showed antithrombotic effects, which are likely due to platelet adhesion and aggregation inhibition as well as anticoagulant activities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
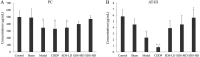
Similar articles
-
Study on the antithrombotic effect and physiological mechanism of okanin.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Sep;153:113358. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113358. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35785699
-
Effects of astaxanthin on blood coagulation, fibrinolysis and platelet aggregation in hyperlipidemic rats.Pharm Biol. 2017 Dec;55(1):663-672. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2016.1261905. Pharm Biol. 2017. PMID: 27951728 Free PMC article.
-
Panax quinquefolius saponins combined with dual antiplatelet drug therapy alleviate gastric mucosal injury and thrombogenesis through the COX/PG pathway in a rat model of acute myocardial infarction.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 27;13(3):e0194082. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194082. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29584740 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the antithrombotic activity of Zhi-Xiong Capsules, a Traditional Chinese Medicinal formula, via the pathway of anti-coagulation, anti-platelet activation and anti-fibrinolysis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jan;97:1622-1631. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.135. Epub 2017 Dec 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29793324
-
Correlation of Platelet and Coagulation Function with Blood Stasis Syndrome in Coronary Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Chin J Integr Med. 2021 Nov;27(11):858-866. doi: 10.1007/s11655-021-2871-2. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Chin J Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 34532747
Cited by
-
Mechanism and Potential Target of Blood-Activating Chinese Botanical Drugs Combined With Anti-Platelet Drugs: Prevention and Treatment of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 3;13:811422. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.811422. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35721128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Effects of Plant Extracts from Salvia deserta Schang. and Salvia sclarea L.Plants (Basel). 2022 Oct 12;11(20):2690. doi: 10.3390/plants11202690. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297710 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Compounds of Salvia L. Genus and Molecular Mechanism of Their Biological Activity.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 27;11(12):3151. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123151. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biology of medicinal resource substitution in Salvia.Chin Med. 2021 Dec 23;16(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s13020-021-00548-6. Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 34949181 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Botany, Phytochemistry, and Biological Activities of Eight Salvia Species Widespread in Kazakhstan.Molecules. 2025 Mar 3;30(5):1142. doi: 10.3390/molecules30051142. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40076365 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang CS, Chen CS, Yang TT, Lou FC. In vitro Radix salviae miltiorrhizae action on blood anticoagulation and fibrinogenolysis. Chin Med J (Engl). 1978;4:123–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

