D1 dopamine receptors intrinsic activity and functional selectivity affect working memory in prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 30532019
- PMCID: PMC9710464
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-018-0312-1
D1 dopamine receptors intrinsic activity and functional selectivity affect working memory in prefrontal cortex
Abstract
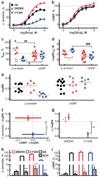
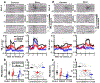
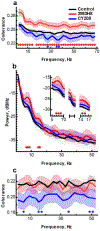
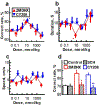
Dopamine D1 agonists enhance cognition, but the role of different signaling pathways (e.g., cAMP or β-arrestin) is unclear. The current study compared 2-methyldihydrexidine and CY208,243, drugs with different degrees of both D1 intrinsic activity and functional selectivity. 2-Methyldihydrexidine is a full agonist at adenylate cyclase and a super-agonist at β-arrestin recruitment, whereas CY208,243 has relatively high intrinsic activity at adenylate cyclase, but much lower at β-arrestin recruitment. Both drugs decreased, albeit in dissimilar ways, the firing rate of neurons in prefrontal cortex sensitive to outcome-related aspects of a working memory task. 2-Methyldihydrexidine was superior to CY208,243 in prospectively enhancing similarity and retrospectively distinguishing differences between correct and error outcomes based on firing rates, enhancing the micro-network measured by oscillations of spikes and local field potentials, and improving behavioral performance. This study is the first to examine how ligand signaling bias affects both behavioral and neurophysiological endpoints in the intact animal. The data show that maximal enhancement of cognition via D1 activation occurred with a pattern of signaling that involved full unbiased intrinsic activity, or agonists with high β-arrestin activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interested:
RBM has a potential conflict-of-interest related to his role as an inventor on patents related to dopamine D1 agonists, the ownership of which has been assigned to university foundations. These issues are managed by the Conflict-of-Interest system at the Penn State University and its College of Medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dose-Dependent Regulation on Prefrontal Neuronal Working Memory by Dopamine D1 Agonists: Evidence of Receptor Functional Selectivity-Related Mechanisms.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jun 16;16:898051. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.898051. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35784852 Free PMC article.
-
A Dopamine D1 Agonist Versus Methylphenidate in Modulating Prefrontal Cortical Working Memory.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2022 Aug;382(2):88-99. doi: 10.1124/jpet.122.001215. Epub 2022 Jun 5. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2022. PMID: 35661631 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of behavioral changes in T-maze alternation from dopamine D1 agonists with different receptor coupling mechanisms.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2023 Oct;240(10):2187-2199. doi: 10.1007/s00213-023-06440-5. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2023. PMID: 37578525 Free PMC article.
-
Under the curve: critical issues for elucidating D1 receptor function in working memory.Neuroscience. 2006 Apr 28;139(1):263-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.09.028. Epub 2005 Nov 28. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16310964 Review.
-
Functional significance of central D1 receptors in cognition: beyond working memory.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2012 Jul;32(7):1248-58. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2011.194. Epub 2012 Jan 11. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2012. PMID: 22234338 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Selectivity of Dopamine D1 Receptor Signaling: Retrospect and Prospect.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 3;22(21):11914. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111914. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-Arrestins: Structure, Function, Physiology, and Pharmacological Perspectives.Pharmacol Rev. 2023 Sep;75(5):854-884. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.121.000302. Epub 2023 Apr 7. Pharmacol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37028945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopamine D1 Receptor Agonists Rescue Age-related Decline in Temporal Order Memory.Neuroscience. 2024 Jul 23;551:177-184. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2024.05.033. Epub 2024 May 31. Neuroscience. 2024. PMID: 38823551 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Pharmacological Evaluation of Noncatechol G Protein Biased and Unbiased Dopamine D1 Receptor Agonists.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2019 Apr 5;10(5):792-799. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00050. eCollection 2019 May 9. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2019. Retraction in: ACS Med Chem Lett. 2022 May 17;13(6):989. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00197. PMID: 31098001 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
D1, not D2, dopamine receptor activation dramatically improves MPTP-induced parkinsonism unresponsive to levodopa.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 5;892:173760. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173760. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33279520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang Y, Mailman RB. Strategic neuronal encoding in medial prefrontal cortex of spatial working memory in the T-maze. Behav Brain Res 2018; 343: 50–60. - PubMed
-
- Vijayraghavan S, Wang M, Birnbaum SG, Williams GV, Arnsten AF. Inverted-U dopamine D1 receptor actions on prefrontal neurons engaged in working memory. Nat Neurosci 2007; 10(3): 376–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

