Giant Axonal Neuropathy: Clinical, Radiological, and Genetic Features
- PMID: 30532362
- PMCID: PMC6238561
- DOI: 10.4103/aian.AIAN_82_18
Giant Axonal Neuropathy: Clinical, Radiological, and Genetic Features
Abstract
Introduction: Giant axonal neuropathy (GAN) is an inherited neurodegenerative disorder caused by mutations in the GAN gene. It affects both the central and peripheral nervous systems. We discuss clinical, electrophysiological, radiological and genetic features in three new unrelated patients with GAN.
Methods: Three pediatric patients with suspected GAN were included. The diagnosis was considered in patients with early onset polyneuropathy and characteristic hair with central nervous system involvement or suggestive neuroimaging findings. Biochemical, metabolic and electrophysiological investigations were performed. Diagnosis was confirmed by targeted sequencing of the GAN gene.
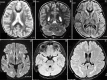
Results: All the three patients were found to have biallelic mutations in GAN gene. Peripheral neuropathy, characteristic hair, and cerebellar dysfunction were present in all three while bony deformities, cranial nerve involvement and intellectual disability were seen variably. Neuroimaging showed a spectrum of findings which are discussed.
Conclusion: GAN is a clinically and radiologically heterogeneous disease where genetic testing is necessary for a definite diagnosis and counselling. With facilities for testing becoming increasingly available, the spectrum is likely to expand further.
Keywords: GAN; Giant axonal neuropathy; gigaxonin; hereditary neuropathy; magnetic resonance imaging; sensory neuropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expanding the genetic spectrum of giant axonal neuropathy: Two novel variants in Iranian families.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2023 Jun;11(6):e2159. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.2159. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2023. PMID: 36866531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Giant Axonal Neuropathy: A Case Report of Subclinical Childhood Manifestations.Cureus. 2024 Feb 17;16(2):e54368. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54368. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38500911 Free PMC article.
-
Giant axonal neuropathy.Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;115:933-8. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-52902-2.00052-7. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23931822 Review.
-
Giant axonal neuropathy: a multicenter retrospective study with genotypic spectrum expansion.Neurogenetics. 2020 Jan;21(1):29-37. doi: 10.1007/s10048-019-00596-z. Epub 2019 Oct 26. Neurogenetics. 2020. PMID: 31655922
-
Giant axonal neuropathy (GAN) in an 8-year-old girl caused by a homozygous pathogenic splicing variant in GAN gene.Am J Med Genet A. 2022 Mar;188(3):836-846. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62592. Epub 2021 Dec 10. Am J Med Genet A. 2022. PMID: 34889507
Cited by
-
Expanding the genetic spectrum of giant axonal neuropathy: Two novel variants in Iranian families.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2023 Jun;11(6):e2159. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.2159. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2023. PMID: 36866531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expanding the genotype-phenotype correlation of childhood sensory polyneuropathy of genetic origin.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 30;10(1):16184. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73219-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32999401 Free PMC article.
-
Giant axonal neuropathy: a rare inherited neuropathy with a novel mutation.Neurogenetics. 2024 Nov 27;26(1):11. doi: 10.1007/s10048-024-00790-8. Neurogenetics. 2024. PMID: 39602023
-
Genetic Approaches for the Treatment of Giant Axonal Neuropathy.J Pers Med. 2022 Dec 30;13(1):91. doi: 10.3390/jpm13010091. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36675752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Normative Observational Nerve Ultrasound Values in School-Age Children and Adolescents and Their Application to Hereditary Neuropathies.Front Neurol. 2020 Apr 28;11:303. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00303. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32411079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuhlenbaumer G, Timmerman V, Bomont P. Giant axonal neuropathy. Gene Rev 2013 (updated 2014) In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Stephens K, et al., editors. GeneReviews®. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2016.
-
- Asbury AK, Gale MK, Cox SC, Baringer JR, Berg BO. Giant axonal neuropathy – A unique case with segmental neurofilamentous masses. Acta Neuropathol. 1972;20:237–47. - PubMed
-
- Sabatelli M, Bertini E, Ricci E, Salviati G, Magi S, Papacci M, et al. Peripheral neuropathy with giant axons and cardiomyopathy associated with desmin type intermediate filaments in skeletal muscle. J Neurol Sci. 1992;109:1–0. - PubMed
-
- Fabrizi GM, Cavallaro T, Angiari C, Bertolasi L, Cabrini I, Ferrarini M, et al. Giant axon and neurofilament accumulation in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2E. Neurology. 2004;62:1429–31. - PubMed
-
- Akagi M, Mohri I, Iwatani Y, Kagitani-Shimono K, Okinaga T, Sakai N, et al. Clinicogenetical features of a Japanese patient with giant axonal neuropathy. Brain Dev. 2012;34:156–62. - PubMed

