Selenium as a pleiotropic agent for medical discovery and drug delivery
- PMID: 30532534
- PMCID: PMC6241719
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S181343
Selenium as a pleiotropic agent for medical discovery and drug delivery
Abstract
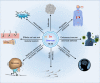
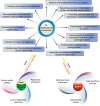
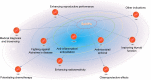
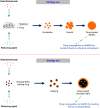
Selenium as a biologically active element lends much support to health maintenance and disease prevention. It is now presenting pleiotropic effects on therapy and drug delivery. In this study, a profiling on the physiological functions, therapeutic significances, clinical/preclinical performances, and biomedical and drug delivery applications of selenium in different modalities was carried out. Major interests focused on selenium-based nanomedicines in confronting various diseases pertaining to selenium or not, especially in antitumor and antidiabetes. Furthermore, the article exclusively discusses selenium nanoparticles featured by ameliorative functions with emphasis on their applications in medical practice and drug delivery. The state-of-the-art in medical discovery as well as research and development on selenium and nano-selenium is discussed in this review.
Keywords: biomedical applications; diabetes; drug delivery; nanomedicine; oncotherapy; selenium; selenium nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nano-selenium and its nanomedicine applications: a critical review.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Apr 10;13:2107-2128. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S157541. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29692609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicines as cancer therapeutics: current status.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013 May;13(4):362-78. doi: 10.2174/1568009611313040002. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 23517593 Review.
-
Nanomedicine for Intranasal Delivery to Improve Brain Uptake.Curr Drug Deliv. 2018;15(4):461-469. doi: 10.2174/1567201814666171013150534. Curr Drug Deliv. 2018. PMID: 29034836 Review.
-
Selenium nanoparticles: potential in cancer gene and drug delivery.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017 May;12(9):1075-1089. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2017-0024. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28440710 Review.
-
Pharmacokinetics, Metabolism, Distribution and Permeability of Nanomedicine.Curr Drug Metab. 2018;19(4):327-334. doi: 10.2174/1389200219666180305154119. Curr Drug Metab. 2018. PMID: 29512450 Review.
Cited by
-
Selenium: An Antioxidant with a Critical Role in Anti-Aging.Molecules. 2022 Oct 5;27(19):6613. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196613. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles in Biomedical Sciences: Properties, Current Trends, Novel Opportunities and Emerging Challenges in Theranostic Nanomedicine.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Jan 19;13(3):424. doi: 10.3390/nano13030424. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36770385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Theranostic Advances of Bionanomaterials against Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Preliminary Review.J Funct Biomater. 2021 Sep 28;12(4):54. doi: 10.3390/jfb12040054. J Funct Biomater. 2021. PMID: 34698244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ca2+-Dependent Effects of the Selenium-Sorafenib Nanocomplex on Glioblastoma Cells and Astrocytes of the Cerebral Cortex: Anticancer Agent and Cytoprotector.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 26;24(3):2411. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032411. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768736 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of the Technique for Obtaining Selenium Nanoparticles Stabilized with Cocamidopropyl Betaine.Russ J Gen Chem. 2022;92(12):2939-2943. doi: 10.1134/S1070363222120489. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Russ J Gen Chem. 2022. PMID: 36778663 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davy T, Castellano S. The genomics of selenium: Its past, present and future. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018 May 30; Epub. - PubMed
-
- Duntas LH, Benvenga S. Selenium: an element for life. Endocrine. 2015;48(3):756–775. - PubMed
-
- Kieliszek M, Błażejak S. Selenium: Significance, and outlook for supplementation. Nutrition. 2013;29(5):713–718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

