Antidiabetic Effects of the Ethanolic Root Extract of Uvaria chamae P. Beauv (Annonaceae) in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats: A Potential Alternative Treatment for Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 30532775
- PMCID: PMC6250042
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/1314941
Antidiabetic Effects of the Ethanolic Root Extract of Uvaria chamae P. Beauv (Annonaceae) in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats: A Potential Alternative Treatment for Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
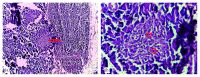
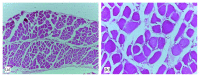
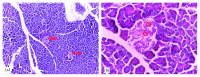
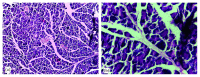
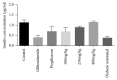
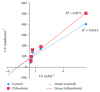
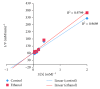
Diabetes mellitus has been a menace to mankind from time immemorial. However, a natural product such as U. chamae P. Beauv (Annonaceae) offers alternative treatment for diabetes mellitus. The study aimed at evaluating antidiabetic activity of the ethanolic root extract of U. chamae in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes was induced in Sprague Dawley rats after overnight fast with 150 mg/kg alloxan intraperitoneally. After 72 h, those with plasma glucose levels >200 mg/dl were classified as diabetic. Five diabetic rats in each group were treated daily for 14 days orally with 100, 250, and 400 mg/kg of the extract, glibenclamide (71 µg/kg) and pioglitazone (429 µg/kg), respectively, while another group was untreated. Control received 0.5 ml of Acacia senegal. Effects of extract on glucose, other biochemical, and hematological parameters were evaluated. α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of extract and its fractions were also evaluated. Percentage inhibition and IC50 values were determined. Diabetic control was achieved on the 7th day of the study with 100, 250, and 400 mg/kg of the extract showing glucose reduction of 72.14%, 78.75%, and 87.71%, respectively. The HDL-cholesterol levels of diabetic rats treated with extracts were significantly increased. Extract and its fractions caused α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibition. Histologically, pancreas of diabetic rats treated with extract showed regenerated islet cells which were not seen in rats treated with glibenclamide and pioglitazone. This study showed that U. chamae has antidiabetic activity which may be through α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibition and regeneration of pancreatic beta cells. Also, it may reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by increasing HDL-cholesterol levels.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Antidiabetic and hypolipidemic activities of hydroethanolic root extract of Uvaria chamae in streptozotocin induced diabetic albino rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Nov 15;16(1):468. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1450-0. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27846886 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Uvaria chamae Root Extracts on Blood Glucose, Inflammatory Markers, Lipid Profile, Liver and Renal Status in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rats.Niger J Physiol Sci. 2019 Dec 31;34(2):207-213. Niger J Physiol Sci. 2019. PMID: 32343272
-
Effect of ethanolic extract of Cassia occidentalis Linn. for the management of alloxan-induced diabetic rats.Pharmacognosy Res. 2010 May;2(3):132-7. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.65506. Pharmacognosy Res. 2010. PMID: 21808555 Free PMC article.
-
Possible antidiabetic and antihyperlipidaemic effect of fermented Parkia biglobosa (JACQ) extract in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2006 Sep;33(9):808-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2006.04444.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16922811
-
Evaluation of the Antidiabetic Activities of the Fruit of Parquetina nigrescens (Afzel.) Bullock and In Silico Identification of Its Antidiabetic Agent.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2024 Jan 26;18:11779322231223857. doi: 10.1177/11779322231223857. eCollection 2024. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2024. PMID: 38283284 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-diabetic compounds from Uvaria dulcis Dunal.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 28;10(5):e26962. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26962. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38463830 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Plantain Bulb's Extract-Beverage Blend on Blood Glucose Levels, Antioxidant Status, and Carbohydrate Hydrolysing Enzymes in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats.Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2020 Dec 31;25(4):362-374. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2020.25.4.362. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2020. PMID: 33505930 Free PMC article.
-
GC-MS analysis, pH and antioxidant effect of Ruzu herbal bitters on alloxan-induced diabetic rats.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021 Jun 17;27:101057. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101057. eCollection 2021 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 34179519 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive in-vitro/in-vivo screening toolbox for the elucidation of glucose homeostasis modulating properties of plant extracts (from roots) and its bioactives.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 26;15:1396292. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1396292. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38989154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Ruzu Herbal Bitters on the Liver Function and Lipid Profile Parameters of Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2024 May-Jun;14(3):100929. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2021.09.012. Epub 2021 Sep 23. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38799007 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Health estimates 2013: Deaths by Cause, Age, Sex and Country, 2000-2012. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2014.
-
- Alberti K. G. M. M., Zimmet P. Z., WHO Consultation Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Provisional report of a WHO Consultation. Diabetic Medicine. 1998;15(7):539–553. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9136(199807)15:7<539::aid-dia668>3.0.co;2-s. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

