A case report of percutaneous successful closure of multiple atrial septal defect
- PMID: 30532904
- PMCID: PMC6265239
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jccase.2011.10.001
A case report of percutaneous successful closure of multiple atrial septal defect
Abstract
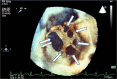
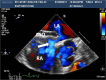
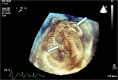
A 50-year-old male patient with a secundum-type atrial septal defect (ASD) suffering from respiratory distress for 7 days was referred to our hospital. Transthoracic echocardiography demonstrated the defects of 9 mm and 4 mm in the middle atrial septum in the parasternal four-chamber view. However, we found not 2, but 6 atrial defects by using real time 3-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography. Open heart surgery was not indicated, because his pulmonary function was poor. After fully informed consent, we decided to treat ASD with Amplatzer septal occluders.
Keywords: Amplatzar septal occluder; Atrial septal defect; Real time 3-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography.
Figures
References
-
- Lin S.M., Tsai S.K., Wang J.K., Han Y.Y., Jean W.H., Yeh Y.C. Supplementing transesophageal echocardiography with transthoracic echocardiography for monitoring transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects with attenuated anterior rim: a case series. Anesth Analg. 2003;96:1584–1588. - PubMed
-
- Acar P. Three-dimensional echocardiography in children with atrial septal defect. Minerva Pediatr. 2004;56:29–40. - PubMed
-
- Acar P., Roux D., Dulac Y., Rougé P., Aggoun Y. Transthoracic three-dimensional echocardiography prior to closure of atrial septal defects in children. Cardiol Young. 2003;13:58–63. - PubMed
-
- Acar P., Massavuau P., Elbaz M. Real-time 3D transoesophageal echocardiography for guiding Amplatzer septal occlude device deployment in an adult patient with atrial septal defect. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2008;9:822–823. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

