A facile fabrication of novel stuff with antibacterial property and osteogenic promotion utilizing red phosphorus and near-infrared light
- PMID: 30533553
- PMCID: PMC6260431
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2018.11.002
A facile fabrication of novel stuff with antibacterial property and osteogenic promotion utilizing red phosphorus and near-infrared light
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding missing Declaration of Competing Interest statements in previously published articles.Bioact Mater. 2020 Dec 4;6(6):1789-1790. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.11.009. eCollection 2021 Jun. Bioact Mater. 2020. PMID: 33336111 Free PMC article.
Abstract
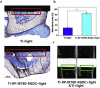
Bone-implant materials are important for bone repairing and orthopedics surgery, which include bone plates and bone nails. These materials need to be designed not only considering its biostability and biocompatibility, but also their by-products induced infection after therapy or long-time treatment in vivo. Thus, the development of novel implant materials is quite urgent. Red phosphorus has great biocompatibility and exhibits efficient photothermal ability. Herein, a red phosphorus/IR780/arginine-glycine-asparticacid-cysteine (RGDC) coating on titanium bone-implant was prepared. The temperature sensitivity of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm is enhanced in the presence of ROS produced by IR780 with 808 nm light irradiation. With keeping the cells and tissues normal, a high antibacterial performance can be realized by near-infrared (808 nm) irradiated within 10 min at 50 °C. Besides the high effective antibacterial efficacy provided by photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT), the RGDC decorated surface can also possess an excellent performance in osteogenesis in vivo.
Keywords: Antibacterial; Biofilm; Implants; Near-infrared; Osteogenesis; Red phosphorus.
Figures




References
-
- Jin G., Qin H., Cao H., Qiao Y., Zhao Y., Peng X., Zhang X., Liu X., Chu Paul K. Zn/Ag micro-galvanic couples formed on titanium and osseointegration effects in the presence of S. aureus. Biomaterials. 2015;65:22–31. - PubMed
-
- Wang J., Zhou H., Guo G., Tan J., Wang Q., Tang J., Liu W., Shen H., Li J., Zhang X. Enhanced anti-infective efficacy of Nano-ZnO films through a combination of intrinsic anti-biofilm activity and reinforced innate defense. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2017;39:33609–33623. - PubMed
-
- Cheng H., Xiong W., Fang Z., Guan H., Wu W., Li Y., Zhang Y., Alvarez M.M., Gao B., Huo K., Xu J., Xu N., Zhang C., Fu J., Khademhosseini A., Li F. Strontium (Sr) and silver (Ag) loaded nanotubular structures with combined osteoinductive and antimicrobial activities. Acta Biomater. 2016;31:388–400. - PubMed
-
- Li J., Tan L., Liu X., Cui Z., Yang X., Yeung Kelvin W.K., Paul, Chu K., Wu S. Balancing bacteria-osteoblast competition through selective physical puncture and biofunctionalization of ZnO/Polydopamine/Arginine-Glycine-Aspartic Acid-Cysteine nanorods. ACS Nano. 2017;11:11250–11263. - PubMed
-
- Cheng X., Sun R., Yin L., Chai Z., Shi H., Gao M. Light-triggered assembly of gold nanoparticles for photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging of tumors in Vivo. Adv. Mater. 2017;29:1604894. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

