Transient hyperkalemia-induced T-wave oversensing as a cause of inappropriate ICD discharges
- PMID: 30534283
- PMCID: PMC6277601
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jccase.2013.07.008
Transient hyperkalemia-induced T-wave oversensing as a cause of inappropriate ICD discharges
Abstract
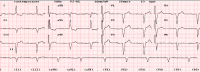
The present case describes a patient with an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) who reported several ICD inappropriate discharges due to transient T-wave oversensing in the setting of acute hyperkalemia. T-wave oversensing was detected only at telemetry interrogation while T-wave amplitude at surface 12-lead electrocardiogram was normal. Oversensing was abolished by reducing potassium levels and by device reprogramming. This case report underscores the importance of identifying a potentially reversible cause of ICD inappropriate discharges and the utility of careful review of stored electrograms. <Learning objective: This case report underscores the importance of understanding the diversity of causes of implantable cardioverter-defibrillator malfunctioning and the utility of careful review of stored electrograms.>.
Keywords: Hyperkalemia; Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator; Inappropriate implantable cardioverter-defibrillator discharges; T-wave oversensing.
Figures



References
-
- Moss A.J., Zareba W., Hall W.J., Kleinh H., Wilber D.J., Cannom D.S., Daubert J.P., Higgins S.L., Brown M.W., Andrews M.L., Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial II Investigators Prophylactic implantation of defibrillator in patients with myocardial infarction and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl Med. 2002;346:877–883. - PubMed
-
- Occhetta E., Bortnik M., Magnani A., Francalacci G., Marino P. Inappropriate implantable cardioverter-defibrillator discharges unrelated to supraventricular tachyarrhythmias. Europace. 2006;8:863–869. - PubMed
-
- Boriani G., Occhetta E., Pistis G., Menozzi C., Jorfida M., Sermasi S., Pagani M., Gasparini G., Musso G., Dall’acqua A., Biffi M., Branzi A. Combined use of morphology discrimination, sudden onset, and stability as discriminating algorithms in single chamber cardioverter defibrillators. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2002;25:1357–1366. - PubMed
-
- Weretka S., Michaelsen J., Becker R., Karle C.A., Voss F., Hilbel T., Osswald B.R., Bahner M.L., Senges J.C., Kuebler W., Schoels W. Ventricular oversensing: a study of 101 patients implanted with dual chamber defibrillators and two different lead systems. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2003;26:65–70. - PubMed
-
- Arthur W., Kaye G.C. Hyperkalemia diagnosed by implantable cardioverter defibrillator T wave sensing. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2001;24:908–909. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

