Neuronal photoactivation through second-harmonic near-infrared absorption by gold nanoparticles
- PMID: 30534369
- PMCID: PMC6279767
- DOI: 10.1038/s41377-018-0103-0
Neuronal photoactivation through second-harmonic near-infrared absorption by gold nanoparticles
Abstract
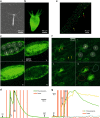
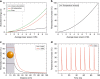
Optical activation of neurons requires genetic manipulation or the use of chemical photoactivators with undesirable side effects. As a solution to these disadvantages, here, we demonstrate optically evoked neuronal activity in mouse cortical neurons in acute slices and in vivo by nonlinear excitation of gold nanoparticles. In addition, we use this approach to stimulate individual epitheliomuscular cells and evoke body contractions in Hydra vulgaris. To achieve this, we use a low-power pulsed near-infrared excitation at the double-wavelength of the plasmon resonance of gold nanoparticles, which enables optical sectioning and allows for high spatial precision and large penetration depth. The effect is explained by second-harmonic Mie scattering, demonstrating light absorption by a second-order nonlinear process, which enables photothermal stimulation of the cells. Our approach also minimizes photodamage, demonstrating a major advancement towards precise and harmless photoactivation for neuroscience and human therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine.J Phys Chem B. 2006 Apr 13;110(14):7238-48. doi: 10.1021/jp057170o. J Phys Chem B. 2006. PMID: 16599493
-
The potential use of the enhanced nonlinear properties of gold nanospheres in photothermal cancer therapy.Lasers Surg Med. 2007 Oct;39(9):747-53. doi: 10.1002/lsm.20577. Lasers Surg Med. 2007. PMID: 17960762
-
Antibody-conjugated gold nanoparticles as nanotransducers for second near-infrared photo-stimulation of neurons in rats.Nano Converg. 2022 Mar 21;9(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40580-022-00304-y. Nano Converg. 2022. PMID: 35312875 Free PMC article.
-
Towards minimally invasive deep brain stimulation and imaging: A near-infrared upconversion approach.Neurosci Res. 2020 Mar;152:59-65. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2020.01.005. Epub 2020 Jan 24. Neurosci Res. 2020. PMID: 31987879 Review.
-
Near-IR responsive nanostructures for nanobiophotonics: emerging impacts on nanomedicine.Nanomedicine. 2016 Apr;12(3):771-788. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2015.11.009. Epub 2015 Dec 3. Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 26656629 Review.
Cited by
-
Mid-Infrared Photoacoustic Stimulation of Neurons through Vibrational Excitation in Polydimethylsiloxane.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Sep;11(35):e2405677. doi: 10.1002/advs.202405677. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38994890 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Second Harmonic Imaging of Proton Translocation Through Water Needles in Lipid Membranes.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Jul 24;146(29):19818-19827. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c02810. Epub 2024 Jul 11. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 38991220 Free PMC article.
-
Transient Photoinactivation of Cell Membrane Protein Activity without Genetic Modification by Molecular Hyperthermia.ACS Nano. 2019 Nov 26;13(11):12487-12499. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b01993. Epub 2019 Oct 24. ACS Nano. 2019. PMID: 31613606 Free PMC article.
-
Time for NanoNeuro.Nat Methods. 2021 Nov;18(11):1287-1293. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01270-9. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Nat Methods. 2021. PMID: 34663955 Review.
-
Plasmonic Nanofactors as Switchable Devices to Promote or Inhibit Neuronal Activity and Function.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019 Jul 18;9(7):1029. doi: 10.3390/nano9071029. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31323847 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Righini M, Zelenina AS, Girard C, Quidant R. Parallel and selective trapping in a patterned plasmonic landscape. Nat. Phys. 2007;3:477–480. doi: 10.1038/nphys624. - DOI
-
- Wang Z. Plasmon—resonant gold nanoparticles for cancer optical imaging. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2013;56:506–513. doi: 10.1007/s11433-013-5006-8. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

