Association Between Titin Loss-of-Function Variants and Early-Onset Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 30535219
- PMCID: PMC6436530
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2018.18179
Association Between Titin Loss-of-Function Variants and Early-Onset Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
Importance: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common arrhythmia affecting 1% of the population. Young individuals with AF have a strong genetic association with the disease, but the mechanisms remain incompletely understood.
Objective: To perform large-scale whole-genome sequencing to identify genetic variants related to AF.
Design, setting, and participants: The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute's Trans-Omics for Precision Medicine Program includes longitudinal and cohort studies that underwent high-depth whole-genome sequencing between 2014 and 2017 in 18 526 individuals from the United States, Mexico, Puerto Rico, Costa Rica, Barbados, and Samoa. This case-control study included 2781 patients with early-onset AF from 9 studies and identified 4959 controls of European ancestry from the remaining participants. Results were replicated in the UK Biobank (346 546 participants) and the MyCode Study (42 782 participants).
Exposures: Loss-of-function (LOF) variants in genes at AF loci and common genetic variation across the whole genome.
Main outcomes and measures: Early-onset AF (defined as AF onset in persons <66 years of age). Due to multiple testing, the significance threshold for the rare variant analysis was P = 4.55 × 10-3.
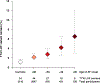
Results: Among 2781 participants with early-onset AF (the case group), 72.1% were men, and the mean (SD) age of AF onset was 48.7 (10.2) years. Participants underwent whole-genome sequencing at a mean depth of 37.8 fold and mean genome coverage of 99.1%. At least 1 LOF variant in TTN, the gene encoding the sarcomeric protein titin, was present in 2.1% of case participants compared with 1.1% in control participants (odds ratio [OR], 1.76 [95% CI, 1.04-2.97]). The proportion of individuals with early-onset AF who carried a LOF variant in TTN increased with an earlier age of AF onset (P value for trend, 4.92 × 10-4), and 6.5% of individuals with AF onset prior to age 30 carried a TTN LOF variant (OR, 5.94 [95% CI, 2.64-13.35]; P = 1.65 × 10-5). The association between TTN LOF variants and AF was replicated in an independent study of 1582 patients with early-onset AF (cases) and 41 200 control participants (OR, 2.16 [95% CI, 1.19-3.92]; P = .01).
Conclusions and relevance: In a case-control study, there was a statistically significant association between an LOF variant in the TTN gene and early-onset AF, with the variant present in a small percentage of participants with early-onset AF (the case group). Further research is necessary to understand whether this is a causal relationship.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosures
Drs. Ellinor and Kathiresan are supported by a grant from Bayer AG to the Broad Institute focused on the genetics and therapeutics of cardiovascular disease. Dr. Lubitz receives sponsored research support from Bristol-Meyers Squibb, Bayer HealthCare, Biotronik, and Boehringer Ingelheim, and has consulted for Abbott and Quest Diagnostics. Dr. Psaty serves on the DSMB of a clinical trial funded by Zoll LifeCor and on the Steering Committee of the Yale Open Data Access Project funded by Johnson & Johnson. Dr. Silverman, in the past three years, received honoraria from Novartis for Continuing Medical Education Seminars and grant and travel support from GlaxoSmithKline. The remaining authors have no disclosures.
Figures

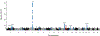

References
-
- Mackay TF. The genetic architecture of quantitative traits. Annu Rev Genet 2001;35:303–339. - PubMed
-
- Manolio TA. Genomewide association studies and assessment of the risk of disease. N Engl J Med 2010;363(2):166–176. - PubMed
-
- Haissaguerre M, Jais P, Shah DC, et al. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med 1998;339(10):659–666. - PubMed
-
- January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2014;64:2246–2280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL139731/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128914/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135818/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA047988/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080467/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K23 HL114724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL127659/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102419/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL105780/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092217/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL068986/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL043851/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085251/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 16EIA26410001/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- R01 HL113338/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL140187/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090620/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL116690/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL093613/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111314/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL139439/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182913/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073410/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R44 TR000045/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 HL099355/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States

