Small Extracellular Vesicles in Rat Serum Contain Astrocyte-Derived Protein Biomarkers of Repetitive Stress
- PMID: 30535257
- PMCID: PMC6403096
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyy098
Small Extracellular Vesicles in Rat Serum Contain Astrocyte-Derived Protein Biomarkers of Repetitive Stress
Abstract
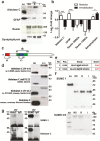
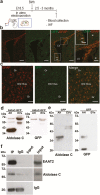
Background: Stress precipitates mood disorders, characterized by a range of symptoms present in different combinations, suggesting the existence of disease subtypes. Using an animal model, we previously described that repetitive stress via restraint or immobilization induced depressive-like behaviors in rats that were differentially reverted by a serotonin- or noradrenaline-based antidepressant drug, indicating that different neurobiological mechanisms may be involved. The forebrain astrocyte protein aldolase C, contained in small extracellular vesicles, was identified as a potential biomarker in the cerebrospinal fluid; however, its specific origin remains unknown. Here, we propose to investigate whether serum small extracellular vesicles contain a stress-specific protein cargo and whether serum aldolase C has a brain origin.
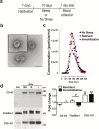
Methods: We isolated and characterized serum small extracellular vesicles from rats exposed to restraint, immobilization, or no stress, and their proteomes were identified by mass spectrometry. Data available via ProteomeXchange with identifier PXD009085 were validated, in part, by western blot. In utero electroporation was performed to study the direct transfer of recombinant aldolase C-GFP from brain cells to blood small extracellular vesicles.
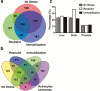
Results: A differential proteome was identified among the experimental groups, including aldolase C, astrocytic glial fibrillary acidic protein, synaptophysin, and reelin. Additionally, we observed that, when expressed in the brain, aldolase C tagged with green fluorescent protein could be recovered in serum small extracellular vesicles.
Conclusion: The protein cargo of serum small extracellular vesicles constitutes a valuable source of biomarkers of stress-induced diseases, including those characterized by depressive-like behaviors. Brain-to-periphery signaling mediated by a differential molecular cargo of small extracellular vesicles is a novel and challenging mechanism by which the brain might communicate health and disease states to the rest of the body.
Keywords: biomarkers; exosomes; stress subtypes.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures
References
-
- Ampuero E, Luarte A, Santibañez M, Varas-Godoy M, Toledo J, Diaz-Veliz G, Cavada G, Rubio FJ, Wyneken U (2015) Two chronic stress models based on movement restriction in rats respond selectively to antidepressant drugs: aldolase C as a potential biomarker. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 18:pyv038. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aydın EP, Genç A, Dalkıran M, Uyar ET, Deniz İ, Özer ÖA, Karamustafalıoğlu KO (2018) Thioredoxin is not a marker for treatment-resistance depression but associated with cognitive function: an rTMS study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 80:322–328. - PubMed
-
- Bruni JE. (1998) Ependymal development, proliferation, and functions: a review. Microsc Res Tech 41:2–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

