Atorvastatin downregulates HSP22 expression in an atherosclerotic model in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 30535427
- PMCID: PMC6317682
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.4015
Atorvastatin downregulates HSP22 expression in an atherosclerotic model in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
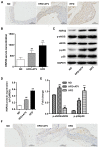
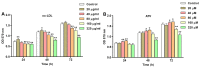
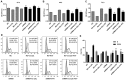
One of the pathological functions of heat shock protein 22 (HSP22) is the association with inflammatory diseases and atherosclerosis. However, the effects of a high‑fat diet (HFD) or oxidized low‑density lipoprotein (ox‑LDL) combined with atorvastatin (ATV) on HSP22 expression are entirely unknown. The present study investigated the effects of ATV on HSP22 expression in HFD‑induced atherosclerotic apolipoprotein E‑deficient (ApoE‑/‑) mice and in ox‑LDL‑induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Furthermore, the influence of HSP22‑knockdown on the HFD- or ox‑LDL‑induced atherosclerotic model was also examined. It was found that HFD or ox‑LDL treatment significantly increased HSP22 expression in the serum and aorta, accompanied by decreased phosphorylated (p)‑endothelial nitric oxide synthase (p-eNOS) activity and activated p38 mitogen‑activated protein kinase (MAPK). However, these effects were suppressed by treatment with ATV. Furthermore, HSP22-knockdown showed reduced ox‑LDL‑induced lesions, evidenced by increased p‑eNOS activity and inactivated p38 MAPK, while suppression of cell proliferation inhibition and cell cycle arrest were also observed. Taken together, the results of this study suggest that HFD or ox‑LDL increased the expression of HSP22 and p‑p38 MAPK, and decreased the p‑eNOS activity in vitro and in vivo, and ATV could reduce the effects by downregulating HSP22 expression.
Figures



References
-
- Cuerrier CM, Chen YX, Tremblay D, Rayner K, McNulty M, Zhao X, Kennedy CR, de BelleRoche J, Pelling AE, O’Brien ER. Chronic overexpression of heat shock protein 27 attenuates atherogenesis and enhances plaque remodeling: A combined histological and mechanical assessment of aortic lesions. PLoS One. 2013;8:e55867. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055867. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smith CC, Yu YX, Kulka M, Aurelian L. A novel human gene similar to the protein kinase (PK) coding domain of the large subunit of herpes simplex virus type 2 ribonucleotide reductase (ICP10) codes for a serine-threonine PK and is expressed in melanoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:25690–25699. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002140200. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

