Subcellular localization of sterol biosynthesis enzymes
- PMID: 30535733
- PMCID: PMC6467513
- DOI: 10.1007/s10735-018-9807-y
Subcellular localization of sterol biosynthesis enzymes
Abstract
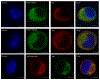
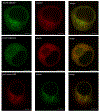
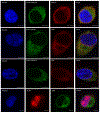
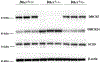
Cholesterol synthesis is a complex, coordinated process involving a series of enzymes. As of today, our understanding of subcellular localization of cholesterol biosynthesis enzymes is far from complete. Considering the complexity and intricacies of this pathway and the importance of functions of DHCR7, DHCR24 and EBP enzymes for human health, we undertook a study to determine their subcellular localization and co-localization. Using expression constructs and antibody staining in cell cultures and transgenic mice, we found that all three enzymes are expressed in ER and nuclear envelope. However, their co-localization was considerably different across the cellular compartments. Furthermore, we observed that in the absence of DHCR7 protein, DHCR24 shows a compensatory upregulation in a Dhcr7-/- transgenic mouse model. The overall findings suggest that the sterol biosynthesis enzymes might not always work in a same functional complex, but that they potentially have different, multifunctional roles that go beyond the sterol biosynthesis pathway. Furthermore, the newly uncovered compensatory mechanism between DHCR7 and DHCR24 could be of importance for designing medications that would improve cholesterol production in patients with desmosterolosis and Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome.
Keywords: 7-Dehydrocholesterol; 8-Dehydrocholesterol; DHCR24; DHCR7; Desmosterol; EBP.
Figures


References
-
- Batta AK, Tint GS, Shefer S, Abuelo D, Salen G (1995) Identification of 8-dehydrocholesterol (cholesta-5,8-dien-3 beta-ol) in patients with Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome J Lipid Res 36:705–713 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

