Increased levels of serum pigment epithelium-derived factor aggravate proteinuria via induction of podocyte actin rearrangement
- PMID: 30536192
- PMCID: PMC6394770
- DOI: 10.1007/s11255-018-2026-3
Increased levels of serum pigment epithelium-derived factor aggravate proteinuria via induction of podocyte actin rearrangement
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the role of serum pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) in the occurrence and development of proteinuria and renal dysfunction and determine its relevant signaling pathway.
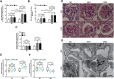
Methods: We analyzed serum PEDF, creatinine, the urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio, and renal morphology of normal or streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice, before and after treatment with PEDF. In vitro, podocytes were stimulated with PEDF under normal or high-glucose conditions; permeability was measured by the transwell assay with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-dextran; and F-actin cytoskeleton was analyzed by phalloidin staining. Apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry. RhoA activity and ROCK1, ZO-1, nephrin, and podocin levels were detected by Western blotting.
Results: Diabetic mice exhibited a high serum PEDF level. In vivo, elevated serum PEDF led to proteinuria, increased serum creatinine, and podocyte foot process fusion in normal or diabetic mice. In vitro, both high-glucose and PEDF stimulation activated the RhoA/ROCK1 pathway in podocytes and promoted cell permeability, F-actin rearrangement, and apoptosis. Inhibition of RhoA/ROCK1 alleviated the damage from these effects.
Conclusions: Elevated serum PEDF aggravates the development of proteinuria and renal dysfunction by inducing F-actin arrangement, foot process fusion, and apoptosis of podocytes in both normal and diabetic mice, and this effect may be mediated by activation of the RhoA/ROCK1 pathway.
Keywords: Actin; Diabetic kidney disease; PEDF; Proteinuria; RhoA/ROCK1.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Salutary effect of pigment epithelium-derived factor in diabetic nephropathy: evidence for antifibrogenic activities.Diabetes. 2006 Jun;55(6):1678-85. doi: 10.2337/db05-1448. Diabetes. 2006. PMID: 16731830
-
Protective role of small pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) peptide in diabetic renal injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013 Sep 15;305(6):F891-900. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00149.2013. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23884140 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) reduces proteinuria by suppressing decreased nephrin and increased VEGF expression in the glomeruli of adriamycin-injected rats.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009 May;24(5):1397-406. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn659. Epub 2008 Nov 28. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009. PMID: 19042927
-
PEDF and septic shock.Curr Mol Med. 2010 Apr;10(3):312-6. doi: 10.2174/156652410791065246. Curr Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20236051 Review.
-
Research progress of natural active compounds on improving podocyte function to reduce proteinuria in diabetic kidney disease.Ren Fail. 2023;45(2):2290930. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2290930. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Ren Fail. 2023. PMID: 38073545 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Various Roles of PEDF in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 24;16(3):510. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030510. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomics and Incident Kidney Failure in Individuals With CKD: The African American Study of Kidney Disease and Hypertension and the Boston Kidney Biopsy Cohort.Kidney Med. 2024 Oct 16;6(12):100921. doi: 10.1016/j.xkme.2024.100921. eCollection 2024 Dec. Kidney Med. 2024. PMID: 39634331 Free PMC article.
-
C1q/TNF-Related Protein-3 (CTRP-3) and Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF) Concentrations in Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study.J Clin Med. 2020 Aug 10;9(8):2587. doi: 10.3390/jcm9082587. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32785102 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Transient Receptor Potential Canonical Channel 6 (TRPC6) in Diabetic Kidney Disease by Regulating Podocyte Actin Cytoskeleton Rearrangement.J Diabetes Res. 2020 Jan 3;2020:6897390. doi: 10.1155/2020/6897390. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 31998809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Rab-Rabphilin system in injured human podocytes stressed by glucose overload and angiotensin II.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 Aug 1;319(2):F178-F191. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00077.2020. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32567349 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

