Evaluating the performance of a deep learning-based computer-aided diagnosis (DL-CAD) system for detecting and characterizing lung nodules: Comparison with the performance of double reading by radiologists
- PMID: 30536611
- PMCID: PMC6360226
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.12931
Evaluating the performance of a deep learning-based computer-aided diagnosis (DL-CAD) system for detecting and characterizing lung nodules: Comparison with the performance of double reading by radiologists
Abstract
Background: The study was conducted to evaluate the performance of a state-of-the-art commercial deep learning-based computer-aided diagnosis (DL-CAD) system for detecting and characterizing pulmonary nodules.
Methods: Pulmonary nodules in 346 healthy subjects (male: female = 221:125, mean age 51 years) from a lung cancer screening program conducted from March to November 2017 were screened using a DL-CAD system and double reading independently, and their performance in nodule detection and characterization were evaluated. An expert panel combined the results of the DL-CAD system and double reading as the reference standard.
Results: The DL-CAD system showed a higher detection rate than double reading, regardless of nodule size (86.2% vs. 79.2%; P < 0.001): nodules ≥ 5 mm (96.5% vs. 88.0%; P = 0.008); nodules < 5 mm (84.3% vs. 77.5%; P < 0.001). However, the false positive rate (per computed tomography scan) of the DL-CAD system (1.53, 529/346) was considerably higher than that of double reading (0.13, 44/346; P < 0.001). Regarding nodule characterization, the sensitivity and specificity of the DL-CAD system for distinguishing solid nodules > 5 mm (90.3% and 100.0%, respectively) and ground-glass nodules (100.0% and 96.1%, respectively) were close to that of double reading, but dropped to 55.5% and 93%, respectively, when discriminating part solid nodules.
Conclusion: Our DL-CAD system detected significantly more nodules than double reading. In the future, false positive findings should be further reduced and characterization accuracy improved.
Keywords: Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD); deep learning based computer-aided diagnosis (DL-CAD); double reading; lung nodule screening; nodule characterization.
© 2018 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
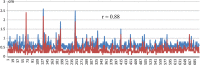
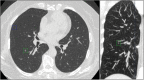
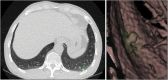
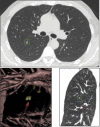
 ) CAD and (
) CAD and ( ) manually.
) manually.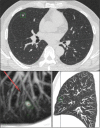
References
-
- World Health Organization . Cancer Fact sheet No 297 2013. [Cited 23 Nov 2018.] Available from URL: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer
-
- Stewart B, Wild C. World Cancer Report 2014. 2015. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon.
-
- International Early Lung Cancer Action Program Investigators , Henschke CI, Yankelevitz DF et al Survival of patients with stage I lung cancer detected on CT screening. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 1763–71. - PubMed
-
- Li F, Sone S, Abe H, MacMahon H, Armato SG III, Doi K. Lung cancers missed at low‐dose helical CT screening in a general population: Comparison of clinical, histopathologic, and imaging findings. Radiology 2002; 225: 673–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

