Multitarget therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 30539809
- PMCID: PMC6334608
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.245463
Multitarget therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
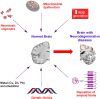
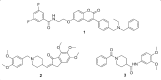
Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, Huntington's and Parkinson's diseases have multifaceted nature because of the different factors contributing to their progression. The complex nature of neurodegenerative diseases has developed a pressing need to design multitarget-directed ligands to address the complementary pathways involved in these diseases. The major enzyme targets for development of therapeutics for Alzheimer's disease are cholinesterase and β-secretase enzymes. In this review, we discuss recent advances in profiling single target inhibitors based on these enzymes to multitarget-directed ligands as potential therapeutics for this devastating disease. In addition, therapeutics based on iron chelation strategy are discussed as well.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; acetylcholinesterase; brain permeability; hybridization; multitarget-directed ligands; neurodegenerative diseases; tacrine; β-secretase.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Di Martino RM, De Simone A, Andrisano V, Bisignano P, Bisi A, Gobbi S, Rampa A, Fato R, Bergamini C, Perez DI, Martinez A, Bottegoni G, Cavalli A, Belluti F. Versatility of the curcumin scaffold: discovery of potent and balanced dual BACE-1 and GSK-3beta inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2016;59:531–544. - PubMed
-
- Gabr MT, Abdel-Raziq MS. Design and synthesis of donepezil analogues as dual AChE and BACE-1 inhibitors. Bioorg Chem. 2018;80:245–252. - PubMed
-
- Hiremathad A, Keri RS, Esteves AR, Cardoso SM, Chaves S, Santos MA. Novel tacrine-hydroxyphenylbenzimidazole hybrids as potential multitarget drug candidates for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Med Chem. 2018;148:255–267. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources