Mechanisms for the Resolution of Organ Fibrosis
- PMID: 30540232
- PMCID: PMC6383633
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00033.2018
Mechanisms for the Resolution of Organ Fibrosis
Abstract
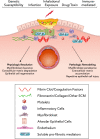
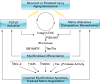
Fibrosis is a dynamic process with the potential for reversibility and restoration of near-normal tissue architecture and organ function. Herein, we review mechanisms for resolution of organ fibrosis, in particular that involving the lung, with an emphasis on the critical roles of myofibroblast apoptosis and clearance of deposited matrix.
Figures

References
-
- Ashley SL, Sisson TH, Wheaton AK, Kim KK, Wilke CA, Ajayi IO, Subbotina N, Wang S, Duckett CS, Moore BB, Horowitz JC. Targeting inhibitor of apoptosis proteins protects from bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 54: 482–492, 2016. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2015-0148OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atabai K, Jame S, Azhar N, Kuo A, Lam M, McKleroy W, Dehart G, Rahman S, Xia DD, Melton AC, Wolters P, Emson CL, Turner SM, Werb Z, Sheppard D. Mfge8 diminishes the severity of tissue fibrosis in mice by binding and targeting collagen for uptake by macrophages. J Clin Invest 119: 3713–3722, 2009. doi: 10.1172/JCI40053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

