Screening of Streptococcus Suis serotype 2 resistance genes with GWAS and transcriptomic microarray analysis
- PMID: 30541452
- PMCID: PMC6292034
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-018-5339-9
Screening of Streptococcus Suis serotype 2 resistance genes with GWAS and transcriptomic microarray analysis
Abstract
Background: Swine streptococcosis has caused great economic loss in the swine industry, and the major pathogen responsible for this disease is Streptococcus Suis serotype 2 (SS2). Disease resistance breeding is a fundamental way of resolving this problem. With the development of GWAS and transcriptomic microarray technology, we now have powerful research tools to identify SS2 resistance genes.
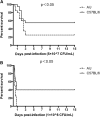
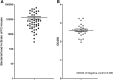
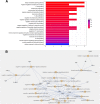
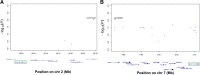
Results: In this research, we generated an F2 generation of SS2 resistant C57BL/6 and SS2 susceptive A/J mice. With the F2 generation of these two mice strains and GWAS analysis, we identified 286 significant mouse genome SNPs sites associated with the SS2 resistance trait. Gene expression profiles for C57BL/6 and A/J were analyzed under SS2 infection pressure by microarray. In total, 251 differentially expressed genes were identified between these two mouse strains during SS2 infection. After combining the GWAS and gene expression profile data, we located two genes that were significantly associated with SS2 resistance, which were the UBA domain containing 1 gene (Ubac1) and Epsin 1 gene (Epn 1). GO classification and over-representation analysis revealed nine up-regulated related to immune function, which could potentially be involved in the C57BL/6 SS2 resistance trait.
Conclusion: This is the first study to use both SNP chip and gene express profile chip for SS2 resistance gene identification in mouse, and these results will contribute to swine SS2 resistance breeding.
Keywords: Genome-wide association study; Resistance genes; Streptococcus suis serotype 2; Transcriptome analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The research was performed in accordance with regulations of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the Nanjing Agricultural University, College of Veterinary Medicine. The Science and Technology Agency of Jiangsu Province approved the protocol. The approval ID is SYXK (SU) 2010–0005.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of candidate susceptibility and resistance genes of mice infected with Streptococcus suis type 2.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032150. Epub 2012 Feb 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22384161 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Pathogenesis of H1N1 Influenza Virus and Swine Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Co-Infection in Pigs by Microarray Analysis.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 23;10(4):e0124086. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124086. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25906258 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus suis serotype 9 strain GZ0565 contains a type VII secretion system putative substrate EsxA that contributes to bacterial virulence and a vanZ-like gene that confers resistance to teicoplanin and dalbavancin in Streptococcus agalactiae.Vet Microbiol. 2017 Jun;205:26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.04.030. Epub 2017 May 1. Vet Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28622857
-
How Streptococcus suis serotype 2 attempts to avoid attack by host immune defenses.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2019 Aug;52(4):516-525. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Mar 27. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2019. PMID: 30954397 Review.
-
Uncovering newly emerging variants of Streptococcus suis, an important zoonotic agent.Trends Microbiol. 2010 Mar;18(3):124-31. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2009.12.003. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Trends Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20071175 Review.
Cited by
-
New Insights From Imputed Whole-Genome Sequence-Based Genome-Wide Association Analysis and Transcriptome Analysis: The Genetic Mechanisms Underlying Residual Feed Intake in Chickens.Front Genet. 2020 Apr 3;11:243. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00243. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32318090 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Effect of Piceatannol on Streptococcus suis Infection Both in vitro and in vivo.Front Microbiol. 2020 Nov 27;11:593588. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.593588. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33329477 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and identification of Streptococcus suis from sick pigs in Bali, Indonesia.BMC Res Notes. 2019 Dec 5;12(1):795. doi: 10.1186/s13104-019-4826-7. BMC Res Notes. 2019. PMID: 31806042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goyette-Desjardins G, Auger JP, Xu J, Segura M, Gottschalk M. Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent-an update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing. Emerging microbes & infections. 2014;3(6):e45. doi: 10.1038/emi.2014.45. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gingles NA, Alexander JE, Kadioglu A, Andrew PW, Kerr A, Mitchell TJ, Hopes E, Denny P, Brown S, Jones HB, et al. Role of genetic resistance in invasive pneumococcal infection: identification and study of susceptibility and resistance in inbred mouse strains. Infect Immun. 2001;69(1):426–434. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.1.426-434.2001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2014ZX0800946B/the National Transgenic Major Program
- 31772746, 31302093, 31272581/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2016YFD0501607/the National Key Research and Development Program
- 201403054/Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest
- BK20130676/the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- KYZ201630/the Key Project of Independent Innovation of the Fundamental Research Fund for the Central Universities of Nanjing Agricultural University
- BE2013433/the Jiangsu Province Science and Technology Support Program
- PAPD/the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
- 201706855039/China Scholarship Council
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

