Middle managers' role in implementing evidence-based practices in healthcare: a systematic review
- PMID: 30541596
- PMCID: PMC6292008
- DOI: 10.1186/s13012-018-0843-5
Middle managers' role in implementing evidence-based practices in healthcare: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Middle managers are in a unique position to promote the implementation of evidence-based practices (EBPs) in healthcare organizations, yet knowledge of middle managers' role in implementation and determinants (e.g., individual-, organizational-, and system-level factors) which influence their role remains fractured, spanning decades and disciplines. To synthesize understanding, we undertook a systematic review of studies of middle managers' role in healthcare EBP implementation and determinants of that role.
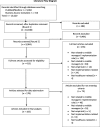
Methods: We searched MEDLINE/PubMed and Business Source Complete (Ebsco) for literature on middle managers' role in healthcare EBP implementation and its determinants. We abstracted data from records that met inclusion criteria (i.e., written in English, peer-reviewed, and reporting either a protocol or results of an empirical study) into a matrix for analysis. We summarized categorical variables using descriptive statistics. To analyze qualitative data, we used a priori codes and then allowed additional themes to emerge.
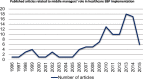
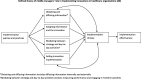
Results: One hundred five records, spanning across several countries and healthcare settings and relating to a range of EBPs, met our inclusion criteria. Studies of middle managers' role in healthcare EBP implementation and its determinants substantially increased from 1996 to 2015. Results from included studies suggest that middle managers shape implementation climate in addition to fulfilling the four roles hypothesized in extant theory of middle managers' role in implementation. However, extant studies offered little understanding of determinants of middle managers' role.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that middle managers may play an important role in facilitating EBP implementation. Included studies offered little understanding regarding the relative importance of various roles, potential moderators of the relationship between middle managers' roles and EBP implementation, or determinants of middle managers' role in EBP implementation. Future studies should seek to understand determinants and moderators of middle managers' role. Clearer understanding may facilitate the translation of evidence into practice.
Keywords: Evidence-based practice; Healthcare; Implementation; Implementation climate; Leader; Middle manager; Supervisor; Systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Our manuscript does not contain any individual person’s data in any form.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Birken SA, Lee S-YD, Weiner BJ, Chin MH, Chiu M, Schaefer C. From strategy to action: how top managers’ support increases middle managers’ commitment to innovation implementation in healthcare organizations. Health Care Manage Rev. 2015;40(2):159–168. doi: 10.1097/HMR.0000000000000018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Currie G, Proctor SJ. The antecedents of middle managers’ strategic contribution: the case of a professional bureaucracy. J Manage Stud. 2005;42(7):1325–1356. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6486.2005.00546.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous