Neostigmine treatment protocols applied in acute colonic pseudo-obstruction disease: A retrospective comparative study
- PMID: 30541715
- PMCID: PMC6428512
- DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2018.18193
Neostigmine treatment protocols applied in acute colonic pseudo-obstruction disease: A retrospective comparative study
Abstract
Background/aims: When conservative methods fail, neostigmine is recommended in the pharmacological treatment of acute colonic pseudo-obstruction (ACPO). The objective of this study was to analyze the response of patients to different neostigmine protocols.
Materials and methods: Patients diagnosed with ACPO in the intensive care unit between January 2015 and September 2017 were retrospectively studied. Either of the two neostigmine protocols, the bolus dose (BD) or continuous infusion (CI), was applied to the ACPO patients who were unresponsive to conservative treatments, and the results were analyzed.
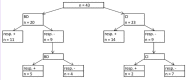
Results: In 79 of 122 (64%) patients, the resolution of symptoms was observed with conservative treatments. Of 43 patients who did not respond to conservative treatments, 20 were applied neostigmine as BD, and 23 were applied by CI. A total of 55% of patients in the BD group and 60.9% patients in the CI group responded to neostigmine therapy after the first dose. The group-specific protocols were reapplied in patients unresponsive to the first dose. A total of 25% in the BD group and 8.7% in the CI group responded to the second dose treatment. As a result, 80% of patients from the BD group and 69.6% from the CI group responded to neostigmine therapy. Although an overall response rate was higher in the BD group, there was no significant difference between groups (P=0.322). Colonic complications were observed in 2 patients, 1 from each group. There were no major side effects requiring treatment cessation.
Conclusion: The safety and effectiveness of both neostigmine protocols applied to ACPO patients were similar. Clinical and radiological responses were obtained without serious side effects with CI.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials