Comment on "ALK is a therapeutic target for lethal sepsis"
- PMID: 30541790
- PMCID: PMC6459396
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aar4321
Comment on "ALK is a therapeutic target for lethal sepsis"
Abstract
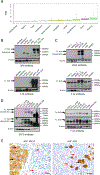
Physiologically relevant ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) expression was not detected in human and mouse monocytes and macrophages, suggesting that the effects of bioactive compounds on stimulator of interferon genes (STING) activation may not depend on ALK.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures

Comment in
-
Response to comment on "ALK is a therapeutic target for lethal sepsis".Sci Transl Med. 2018 Dec 12;10(471):eaas9817. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aas9817. Sci Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30541792
Comment on
-
ALK is a therapeutic target for lethal sepsis.Sci Transl Med. 2017 Oct 18;9(412):eaan5689. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aan5689. Sci Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 29046432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iwahara T et al. , Molecular characterization of ALK, a receptor tyrosine kinase expressed specifically in the nervous system. Oncogene 14, 439–449 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Morris SW et al. , ALK, the chromosome 2 gene locus altered by the t(2;5) in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, encodes a novel neural receptor tyrosine kinase that is highly related to leukocyte tyrosine kinase (LTK). Oncogene 14, 2175–2188 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Chiarle R, Voena C, Ambrogio C, Piva R, Inghirami G, The anaplastic lymphoma kinase in the pathogenesis of cancer. Nature reviews. Cancer 8, 11–23 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Hallberg B, Palmer RH, Mechanistic insight into ALK receptor tyrosine kinase in human cancer biology. Nature reviews. Cancer 13, 685–700 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

