Porcine Hemagglutinating Encephalomyelitis Virus Activation of the Integrin α5β1-FAK-Cofilin Pathway Causes Cytoskeletal Rearrangement To Promote Its Invasion of N2a Cells
- PMID: 30541856
- PMCID: PMC6384086
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01736-18
Porcine Hemagglutinating Encephalomyelitis Virus Activation of the Integrin α5β1-FAK-Cofilin Pathway Causes Cytoskeletal Rearrangement To Promote Its Invasion of N2a Cells
Abstract
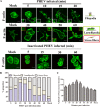
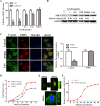
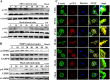
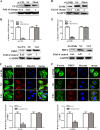
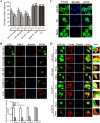
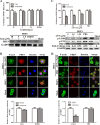
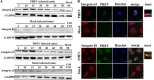
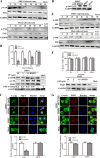
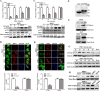
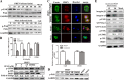
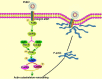
Porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus (PHEV) is a highly neurotropic virus that causes diffuse neuronal infection with neurological damage and high mortality. Virus-induced cytoskeletal dynamics are thought to be closely related to this type of nerve damage. Currently, the regulation pattern of the actin cytoskeleton and its molecular mechanism remain unclear when PHEV enters the host cells. Here, we demonstrate that entry of PHEV into N2a cells induces a biphasic remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton and a dynamic change in cofilin activity. Viral entry is affected by the disruption of actin kinetics or alteration of cofilin activity. PHEV binds to integrin α5β1 and then initiates the integrin α5β1-FAK signaling pathway, leading to virus-induced early cofilin phosphorylation and F-actin polymerization. Additionally, Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1), cell division cycle 42 (Cdc42), and downstream regulatory gene p21-activated protein kinases (PAKs) are recruited as downstream mediators of PHEV-induced dynamic changes of the cofilin activity pathway. In conclusion, we demonstrate that PHEV utilizes the integrin α5β1-FAK-Rac1/Cdc42-PAK-LIMK-cofilin pathway to cause an actin cytoskeletal rearrangement to promote its own invasion, providing theoretical support for the development of PHEV pathogenic mechanisms and new antiviral targets.IMPORTANCE PHEV, a member of the Coronaviridae family, is a typical neurotropic virus that primarily affects the nervous system of piglets to produce typical neurological symptoms. However, the mechanism of nerve damage caused by the virus has not been fully elucidated. Actin is an important component of the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells and serves as the first obstacle to the entry of pathogens into host cells. Additionally, the morphological structure and function of nerve cells depend on the dynamic regulation of the actin skeleton. Therefore, exploring the mechanism of neuronal injury induced by PHEV from the perspective of the actin cytoskeleton not only helps elucidate the pathogenesis of PHEV but also provides a theoretical basis for the search for new antiviral targets. This is the first report to define a mechanistic link between alterations in signaling from cytoskeleton pathways and the mechanism of PHEV invading nerve cells.
Keywords: cofilin; coronavirus; cytoskeletal rearrangement; integrin α5β1; neurotropic virus; porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Porcine Hemagglutinating Encephalomyelitis Virus Enters Neuro-2a Cells via Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis in a Rab5-, Cholesterol-, and pH-Dependent Manner.J Virol. 2017 Nov 14;91(23):e01083-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01083-17. Print 2017 Dec 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28956766 Free PMC article.
-
ATN-161 reduces virus proliferation in PHEV-infected mice by inhibiting the integrin α5β1-FAK signaling pathway.Vet Microbiol. 2019 Jun;233:147-153. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.04.029. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Vet Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31176401
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor-PI3K signaling controls cofilin activity to facilitate herpes simplex virus 1 entry into neuronal cells.mBio. 2014 Jan 14;5(1):e00958-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00958-13. mBio. 2014. PMID: 24425731 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine Hemagglutinating Encephalomyelitis Virus: A Review.Front Vet Sci. 2019 Feb 27;6:53. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00053. eCollection 2019. Front Vet Sci. 2019. PMID: 30873421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenic microbes manipulate cofilin activity to subvert actin cytoskeleton.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2016 Sep;42(5):677-95. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2015.1010139. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 25853495 Review.
Cited by
-
While We Wait for a Vaccine Against SARS-CoV-2, Why Not Think About Available Drugs?Front Physiol. 2020 Jul 3;11:820. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00820. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32719619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small GTPase-A Key Role in Host Cell for Coronavirus Infection and a Potential Target for Coronavirus Vaccine Adjuvant Discovery.Viruses. 2022 Sep 14;14(9):2044. doi: 10.3390/v14092044. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36146850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rho GTPases and the emerging role of tunneling nanotubes in physiology and disease.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Nov 1;319(5):C877-C884. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00351.2020. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32845720 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro whole human proteome cleavage prediction and enrichment/depletion analysis.Comput Biol Chem. 2022 Jun;98:107671. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2022.107671. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Comput Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35429835 Free PMC article.
-
Dabie bandavirus Nonstructural Protein Interacts with Actin to Induce F-Actin Rearrangement and Inhibit Viral Adsorption and Entry.J Virol. 2022 Jul 27;96(14):e0078822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00788-22. Epub 2022 Jul 11. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35862701 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

