Disruption of a self-amplifying catecholamine loop reduces cytokine release syndrome
- PMID: 30542164
- PMCID: PMC6512810
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0774-y
Disruption of a self-amplifying catecholamine loop reduces cytokine release syndrome
Abstract
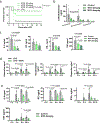
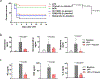
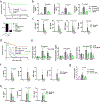
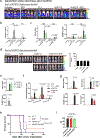
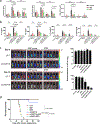
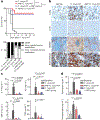
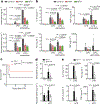
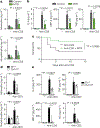
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is a life-threatening complication of several new immunotherapies used to treat cancers and autoimmune diseases1-5. Here we report that atrial natriuretic peptide can protect mice from CRS induced by such agents by reducing the levels of circulating catecholamines. Catecholamines were found to orchestrate an immunodysregulation resulting from oncolytic bacteria and lipopolysaccharide through a self-amplifying loop in macrophages. Myeloid-specific deletion of tyrosine hydroxylase inhibited this circuit. Cytokine release induced by T-cell-activating therapeutic agents was also accompanied by a catecholamine surge and inhibition of catecholamine synthesis reduced cytokine release in vitro and in mice. Pharmacologic catecholamine blockade with metyrosine protected mice from lethal complications of CRS resulting from infections and various biotherapeutic agents including oncolytic bacteria, T-cell-targeting antibodies and CAR-T cells. Our study identifies catecholamines as an essential component of the cytokine release that can be modulated by specific blockers without impairing the therapeutic response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
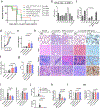
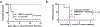
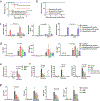
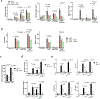

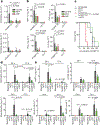
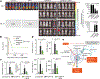
Comment in
-
Adrenaline fuels a cytokine storm during immunotherapy.Nature. 2018 Dec;564(7735):194-196. doi: 10.1038/d41586-018-07581-w. Nature. 2018. PMID: 30542198 No abstract available.
-
Capillary leak syndrome: a cytokine and catecholamine storm?Kidney Int. 2019 May;95(5):1009-1011. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.03.001. Kidney Int. 2019. PMID: 31010471 No abstract available.
-
Epinephrine use in COVID-19: friend or foe?Eur J Hosp Pharm. 2021 Jan;28(1):e1. doi: 10.1136/ejhpharm-2020-002295. Epub 2020 May 29. Eur J Hosp Pharm. 2021. PMID: 32471815 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- van der Poll T, van de Veerdonk FL, Scicluna BP & Netea MG The immunopathology of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Immunol 17, 407–420 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Hansel TT, Kropshofer H, Singer T, Mitchell JA & George AJ The safety and side effects of monoclonal antibodies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 9, 325–338 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Parker BS, Rautela J & Hertzog PJ Antitumour actions of interferons: implications for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 16, 131–144 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

