Protein Kinase C Inhibition Mediates Neuroblast Enrichment in Mechanical Brain Injuries
- PMID: 30542270
- PMCID: PMC6277931
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00462
Protein Kinase C Inhibition Mediates Neuroblast Enrichment in Mechanical Brain Injuries
Abstract
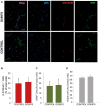
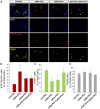
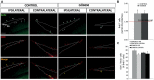
Brain injuries of different etiologies lead to irreversible neuronal loss and persisting neuronal deficits. New therapeutic strategies are emerging to compensate neuronal damage upon brain injury. Some of these strategies focus on enhancing endogenous generation of neurons from neural stem cells (NSCs) to substitute the dying neurons. However, the capacity of the injured brain to produce new neurons is limited, especially in cases of extensive injury. This reduced neurogenesis is a consequence of the effect of signaling molecules released in response to inflammation, which act on intracellular pathways, favoring gliogenesis and preventing recruitment of neuroblasts from neurogenic regions. Protein kinase C (PKC) is a family of intracellular kinases involved in several of these gliogenic signaling pathways. The aim of this study was to analyze the role of PKC isozymes in the generation of neurons from neural progenitor cells (NPCs) in vitro and in vivo in brain injuries. PKC inhibition in vitro, in cultures of NPC isolated from the subventricular zone (SVZ) of postnatal mice, leads differentiation towards a neuronal fate. This effect is not mediated by classical or atypical PKC. On the contrary, this effect is mediated by novel PKCε, which is abundantly expressed in NPC cultures under differentiation conditions. PKCε inhibition by siRNA promotes neuronal differentiation and reduces glial cell differentiation. On the contrary, inhibition of PKCθ exerts a small anti-gliogenic effect and reverts the effect of PKCε inhibition on neuronal differentiation when both siRNAs are used in combination. Interestingly, in cortical brain injuries we have found expression of almost all PKC isozymes found in vitro. Inhibition of PKC activity in this type of injuries leads to neuronal production. In conclusion, these findings show an effect of PKCε in the generation of neurons from NPC in vitro, and they highlight the role of PKC isozymes as targets to produce neurons in brain lesions.
Keywords: PKC; brain injuries; neuroblasts; neurogenesis; neuronal differentiation.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A novel PKC activating molecule promotes neuroblast differentiation and delivery of newborn neurons in brain injuries.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Apr 22;11(4):262. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2453-9. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32321920 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Kinase C: Targets to Regenerate Brain Injuries?Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Mar 20;7:39. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00039. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30949480 Free PMC article.
-
ADAM-17/tumor necrosis factor-α-converting enzyme inhibits neurogenesis and promotes gliogenesis from neural stem cells.Stem Cells. 2011 Oct;29(10):1628-39. doi: 10.1002/stem.710. Stem Cells. 2011. PMID: 21837653
-
Immunopharmacological intervention for successful neural stem cell therapy: New perspectives in CNS neurogenesis and repair.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Jan;141(1):21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.08.001. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 23954656 Review.
-
Brain ischemia, neurogenesis, and neurotrophic receptor expression in primates.Arch Ital Biol. 2011 Jun;149(2):225-31. doi: 10.4449/aib.v149i2.1368. Arch Ital Biol. 2011. PMID: 21701994 Review.
Cited by
-
Network Biology Approaches to Uncover Therapeutic Targets Associated with Molecular Signaling Pathways from circRNA in Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction Pathogenesis.J Mol Neurosci. 2022 Sep;72(9):1875-1901. doi: 10.1007/s12031-022-02042-6. Epub 2022 Jul 6. J Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35792980
-
The subventricular zone neurogenic niche provides adult born functional neurons to repair cortical brain injuries in response to diterpenoid therapy.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jan 5;16(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-04105-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 39757190 Free PMC article.
-
PKC Mediates LPS-Induced IL-1β Expression and Participates in the Pro-inflammatory Effect of A2AR Under High Glutamate Concentrations in Mouse Microglia.Neurochem Res. 2019 Dec;44(12):2755-2764. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02895-1. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Neurochem Res. 2019. PMID: 31650360
-
Rescue of neurogenesis and age-associated cognitive decline in SAMP8 mouse: Role of transforming growth factor-alpha.Aging Cell. 2023 Jun;22(6):e13829. doi: 10.1111/acel.13829. Epub 2023 May 12. Aging Cell. 2023. PMID: 37177826 Free PMC article.
-
A novel PKC activating molecule promotes neuroblast differentiation and delivery of newborn neurons in brain injuries.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Apr 22;11(4):262. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2453-9. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32321920 Free PMC article.

