Population Coding and Correlated Variability in Electrosensory Pathways
- PMID: 30542271
- PMCID: PMC6277784
- DOI: 10.3389/fnint.2018.00056
Population Coding and Correlated Variability in Electrosensory Pathways
Abstract
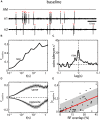
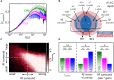
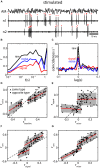
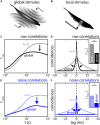
The fact that perception and behavior depend on the simultaneous and coordinated activity of neural populations is well established. Understanding encoding through neuronal population activity is however complicated by the statistical dependencies between the activities of neurons, which can be present in terms of both their mean (signal correlations) and their response variability (noise correlations). Here, we review the state of knowledge regarding population coding and the influence of correlated variability in the electrosensory pathways of the weakly electric fish Apteronotus leptorhynchus. We summarize known population coding strategies at the peripheral level, which are largely unaffected by noise correlations. We then move on to the hindbrain, where existing data from the electrosensory lateral line lobe (ELL) shows the presence of noise correlations. We summarize the current knowledge regarding the mechanistic origins of noise correlations and known mechanisms of stimulus dependent correlation shaping in ELL. We finish by considering future directions for understanding population coding in the electrosensory pathways of weakly electric fish, highlighting the benefits of this model system for understanding the origins and impact of noise correlations on population coding.
Keywords: correlated variability; correlation shaping; electric fish; electrosensory lateral line lobe; feedback; noise correlations; population coding; stimulus encoding.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Population Coding of Natural Electrosensory Stimuli by Midbrain Neurons.J Neurosci. 2021 Apr 28;41(17):3822-3841. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2232-20.2021. Epub 2021 Mar 9. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33687962 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic population coding of natural communication stimuli by hindbrain electrosensory neurons.Sci Rep. 2021 May 25;11(1):10840. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90413-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34035395 Free PMC article.
-
Population coding by electrosensory neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2008 Apr;99(4):1825-35. doi: 10.1152/jn.01266.2007. Epub 2008 Feb 6. J Neurophysiol. 2008. PMID: 18256161 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro studies of closed-loop feedback and electrosensory processing in Apteronotus leptorhynchus.J Physiol Paris. 2008 Jul-Nov;102(4-6):173-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jphysparis.2008.10.012. Epub 2008 Oct 17. J Physiol Paris. 2008. PMID: 18996475 Review.
-
The neuroethology of electrocommunication: how signal background influences sensory encoding and behaviour in Apteronotus leptorhynchus.J Physiol Paris. 2013 Jan-Apr;107(1-2):13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jphysparis.2012.07.001. Epub 2012 Sep 5. J Physiol Paris. 2013. PMID: 22981958 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuronal On- and Off-type heterogeneities improve population coding of envelope signals in the presence of stimulus-induced noise.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 23;10(1):10194. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67258-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32576916 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory Cues Modulate Smooth Pursuit and Active Sensing Movements.Front Behav Neurosci. 2019 Apr 8;13:59. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00059. eCollection 2019. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31024269 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Functions of Feedback in Electrosensory Processing.Front Integr Neurosci. 2019 Sep 13;13:52. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2019.00052. eCollection 2019. Front Integr Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31572137 Free PMC article.
-
Neural populations within macaque early vestibular pathways are adapted to encode natural self-motion.PLoS Biol. 2024 Apr 30;22(4):e3002623. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002623. eCollection 2024 Apr. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 38687807 Free PMC article.
-
Population Coding of Natural Electrosensory Stimuli by Midbrain Neurons.J Neurosci. 2021 Apr 28;41(17):3822-3841. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2232-20.2021. Epub 2021 Mar 9. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33687962 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

