Non-periodized and Daily Undulating Periodized Resistance Training on Blood Pressure of Older Women
- PMID: 30542289
- PMCID: PMC6277793
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01525
Non-periodized and Daily Undulating Periodized Resistance Training on Blood Pressure of Older Women
Abstract
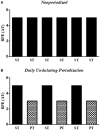
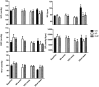
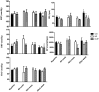
The present study aimed at investigating the effects of a daily undulating periodization (DUP) and non-periodized (NP) resistance training programs on hemodynamic parameters of older women. Forty-two older women were randomized into one of the three experimental groups: NP, DUP, and control group (CG). Evaluations of the hemodynamic parameters occurred before, during and after the intervention. The exercise programs were performed twice a week over 22 weeks. NP and DUP groups were based on 3 sets of 8-10 repetitions in 9 exercises. In NP, the two exercise sessions were based on traditional strength training, which was performed at a Difficult intensity according to the rating of perceived exertion (RPE) method. In DUP, the first session was based on power resistance exercise, in which the concentric muscle contraction was performed as fast as possible at a moderate intensity based on RPE, while the second session was the same that was performed by NP. The findings demonstrated that diastolic blood pressure (90.4 vs. 76.2 mmHg) and mean arterial pressure (108.6 vs. 92.7 mmHg) were significantly reduced after NP, while no significant alterations were observed in DUP. Nevertheless, both training groups seem to have a cardio protective effect, since both training modes prevented the increase in HR reported in the experimental period in CG. In conclusion, our findings indicate that a 22-week NP resistance training program causes beneficial effects on hemodynamic parameters of older women. Trial Registration: NCT03443375.
Keywords: blood pressure; elderly; hypertension; nitric oxide; periodization; physical exercise; power training; strength training.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Periodized and non-periodized resistance training programs on body composition and physical function of older women.Exp Gerontol. 2019 Jul 1;121:10-18. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Mar 9. Exp Gerontol. 2019. PMID: 30862526 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of Powerlifting Performance in Trained Men Using Traditional and Flexible Daily Undulating Periodization.J Strength Cond Res. 2017 Feb;31(2):283-291. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001500. J Strength Cond Res. 2017. PMID: 28129275 Clinical Trial.
-
Application of Session Rating of Perceived Exertion Among Different Models of Resistance Training in Older Adults.J Strength Cond Res. 2015 Dec;29(12):3439-46. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001200. J Strength Cond Res. 2015. PMID: 26595134
-
Effects of Periodization on Strength and Muscle Hypertrophy in Volume-Equated Resistance Training Programs: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Sports Med. 2022 Jul;52(7):1647-1666. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01636-1. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 35044672
-
Short-term Periodization Models: Effects on Strength and Speed-strength Performance.Sports Med. 2015 Oct;45(10):1373-86. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0355-2. Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 26133514 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic Resistance Training Improves Cardiac Autonomic Modulation and Oxidative Stress Parameters in Chronic Stroke Survivors: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Nov 20;2019:5382843. doi: 10.1155/2019/5382843. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31827679 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Combined Aerobic and Resistance Exercises Evokes Longer Reductions on Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Resistant Hypertension: A Randomized Crossover Trial.Cardiovasc Ther. 2020 Jul 20;2020:8157858. doi: 10.1155/2020/8157858. eCollection 2020. Cardiovasc Ther. 2020. PMID: 32821284 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of combined muscle power and endurance training with different volumes on functional and hemodynamic parameters in previously trained older adults.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2023 Nov;35(11):2623-2631. doi: 10.1007/s40520-023-02572-y. Epub 2023 Oct 7. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2023. PMID: 37804402 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Low-Speed and High-Speed Resistance Training Programs on Frailty Status, Physical Performance, Cognitive Function, and Blood Pressure in Prefrail and Frail Older Adults.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Jul 26;8:702436. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.702436. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34381802 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence-based recommendations for resistance and power training to prevent frailty in community-dwellers.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021 Aug;33(8):2069-2086. doi: 10.1007/s40520-021-01802-5. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 33587271 Review.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

